Advantage India
Robust
Demand
* Indian Fintech industry currently is US$ 111 billion and estimated to be at US$ 421 billion by 2029. India has the 3rd largest FinTech ecosystem globally.
* BCG predicts that the proportion of digital payments will grow to 65% by 2026.
* That demand seems particularly strong when it comes to the critical need of protecting consumer data, where incumbent banks have a trust advantage. Some super apps may also turn to banks for access to banking licenses and to meet other regulatory requirements.
Innovation in
Services
* In the recent period, technological innovations have led to marked improvements in efficiency, productivity, quality, inclusion and competitiveness in the extension of financial services, especially in the area of digital lending.
* Digitalization of Agri-finance was conceptualized jointly by the Reserve Bank and the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH). This will enable delivery of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans in a fully digital and hassle-free manner.
* In Union Budget 2025, KYC process to be simplified; revamped Central KYC Registry to be rolled out in 2025.
Business
Fundamentals
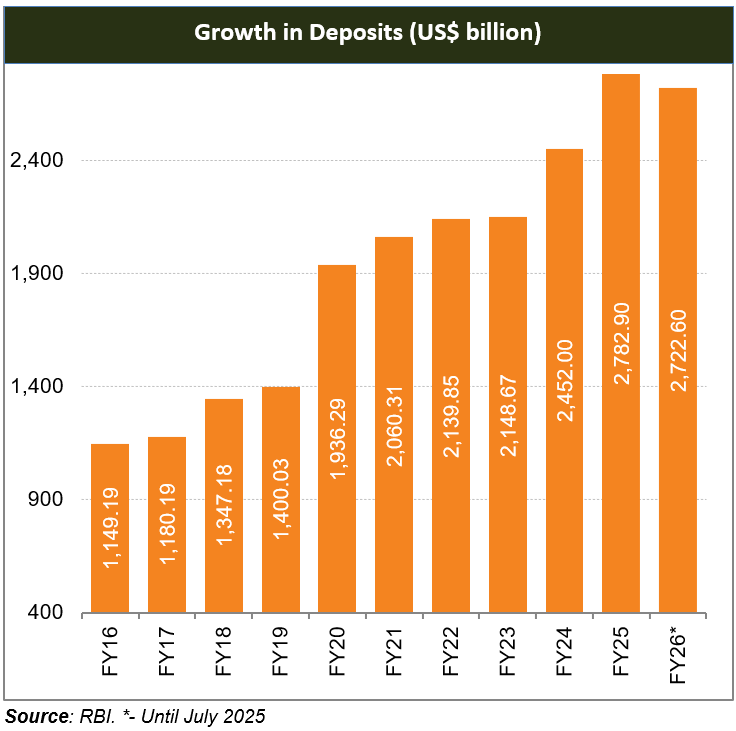
* The Indian banking industry has seen robust growth, driven by strong economic expansion, rising disposable incomes, growing consumerism, and easier credit access.
* Digital modes of payments have grown by leaps and bounds over the last few years.
* In October alone, UPI processed a record Rs. 27.28 lakh crore (US$ 318.48 billion) in value and 20.7 billion transactions, reflecting its deep penetration across users and merchants nationwide.
Policy
Support
* The RBI has launched a pilot to digitalize KCC lending in a bid for efficiency, higher cost savings, and reduction of TAT. This is expected to transform the flow of credit in the rural economy.
* RBI reduced the policy repo rate to 5.5% in June 2025, along with a 25 basis points cut in Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) to support liquidity and lending, which is expected to stimulate demand in the banking sector.
Banking India

Posters
MORE
NEW INDIA DIGITAL INDIA
India will contribute 2.2% to the world's digital payments market by 2023, while the value of such transaction is expected to reach US$ 12.4 trillion globally by 2025.
IBEF Campaigns
MORE
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Utsav 2024
Union Minister of External Affairs, Dr. S. Jaishankar and Union Commerce an...
Case Studies
MOREIBEF BLOG
MOREHow Green Hydrogen Will Shape Renewable Energy in India
Green hydrogen, a superior and a more sustainable alternative to fossil fue...
Cooperatives Rising: How Local Communities Are Shaping India’s Growth
The co-operative movement in India is a strong driving force of inclusive d...
India’s Aspirational Districts: Stories of Progress and People-Led Change
India’s Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) was launched in Januar...