Advantage India
Sector
Overview
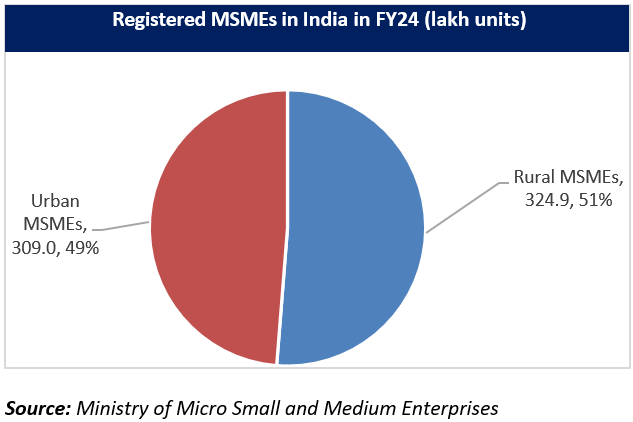
*As on November 20, 2025, 7.16 crore MSMEs, with an employment of 31.33 crore are registered on Udyam Registration Portal and Udyam Assist Platform (UAP).
*The Union Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises has received an allocation of Rs. 23,168 crore (US$ 2.7 billion) in FY26 Union Budget, reflecting a 4.6% increase compared to the FY25 Budget.
Statutory
Bodies
*The MSME Ministry heads five statutory bodies; KVIC, Coir Board, NSIC, NI-MSME and the MGIRI
*These bodies are responsible for aiding MSMEs with respect to government schemes and policies
Government
Schemes
*Under Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), As of April 2025, over Rs. 33,65,000 crore (US$ 390.87 billion) was sanctioned under 52.37 crore Mudra loans to entrepreneurs of SMEs, particularly those belonging to marginal sections of society.
*The "Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance" (RAMP) scheme, launched in 2022, has benefitted 4 lakh micro, small, and medium enterprises, with women-owned businesses making up over 38% of the registered MSMEs, highlighting the government's focus on empowering female entrepreneurs.
Policy
Support
* The Union Budget for FY26 has raised the investment limits for MSMEs by 2.5 times and doubled the turnover thresholds. Specifically, the new limits are as follows:
1. For micro-enterprises, the investment limit is now Rs. 2.5 crore (US$ 0.3 million), with a turnover limit of Rs. 10 crore (US$ 1.2 million).
2. For small enterprises, the investment limit has been set at Rs. 25 crore (US$ 2.9 million), and the turnover limit is Rs. 100 crore (US$ 11.5 million).
3. For medium enterprises, the investment limit is now Rs. 125 crore (US$ 14.4 million), while the turnover limit stands at Rs. 500 crore (US$ 57.6 million).
MSME Clusters
- Maharashtra
- Andhra Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- West Bengal
- Uttar Pradesh
- Kerala

Posters
MORE
CONTRIBUTES ABOUT 29% TOWARDS THE GDP
MSME sector is a major contributor to the socio-economic development of the country.
IBEF Campaigns
MORE
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Utsav 2024
Union Minister of External Affairs, Dr. S. Jaishankar and Union Commerce an...
Case Studies
MOREIBEF BLOG
MORERural Tourism in India: Empowering Villages and Reviving Local Economies
Rural tourism is emerging as a key driver of India’s inclusive growth...
Smart Textiles & Wearables: Weaving Tech into Tradition
The textile industry is dynamically changing. It is no longer a simple nece...
India's Developer Boom: Building the Future with AI and Innovation
India's developer community has reached an inflection point. With 17 mi...