About Indian Economy Growth Rate & Statistics
Introduction
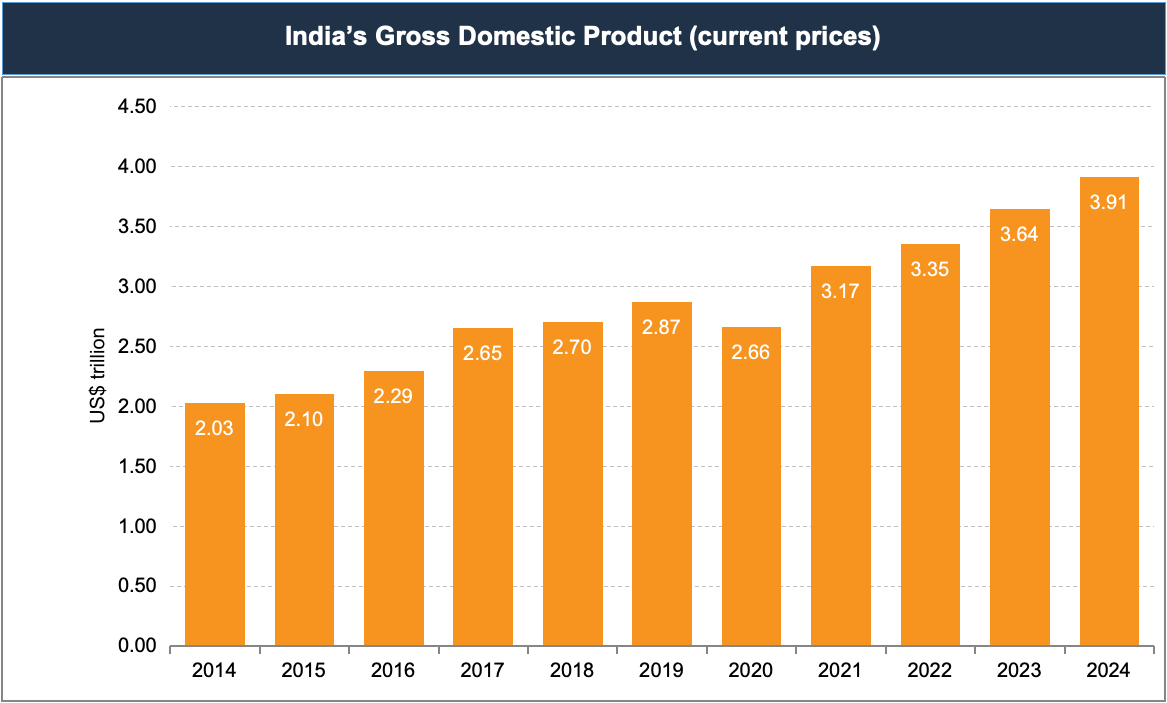
India’s economic journey over the past few years has been marked by remarkable growth and a steady rise in its position on the global stage. After overtaking the United Kingdom (UK) to become the fifth largest economy in Q1 FY23, India has continued this upward trajectory to surpass Japan in June 2025 to become the fourth largest economy in the world. With a nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Rs. 3,31,03,000 crore (US$ 3.78 trillion), India’s growth reflects a combination of strong domestic demand and policy reforms positioning the country as a key destination for global capital.
Further, India is projected to reach a GDP of Rs. 4,26,45,000 crore (US$ 5 trillion) by 2027 and is on course to surpass Germany by 2028. Rising employment and increasing private consumption, supported by rising consumer sentiment, will support GDP growth in the coming months.

Market Overview
India’s Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or GDP at Constant Prices stood at Rs. 47.89 lakh crore (US$ 544.20 billion) in Q1 of FY26, up from Rs. 44.42 lakh crore (US$ 504.77 billion) in Q1 FY25, registering a growth rate of 7.8%. Nominal GDP or GDP at Current Prices for the same period was estimated at Rs. 86.05 lakh crore (US$ 977.84 billion), compared to Rs. 79.08 lakh crore (US$ 898.64 billion) in the corresponding quarter of the previous year, showing a growth rate of 8.8%.
As on October 14, 2025, India is home to 123 unicorns, with six new startups achieving unicorn status in 2025.
India’s current account recorded a deficit of Rs. 21,288 crore (US$ 2.37 billion) in Q1 FY26 (April-June), compared to Rs. 76,282 crore (US$ 8.6 billion) in the same period of FY25, according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The improvement reflects a narrower merchandise trade gap and steady growth in service exports. Exports fared remarkably well during the pandemic and aided recovery when all other growth engines were losing
Source: World Bank
steam in terms of their contribution to GDP. Going forward, the contribution of merchandise exports may waver as several of India’s trade partners witness an economic slowdown. According to Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles Mr. Piyush Goyal, Indian exports are expected to reach US$ 1 trillion by 2030.
Recent Developments
India is primarily a domestic demand-driven economy, with consumption and investments contributing to 70% of the economic activity. With India’s economy showing resilient growth, supported by strong domestic demand, policy reforms, and a healthy investment pipeline, several new projects and developments are underway across key sectors. According to World Bank, India must continue to prioritise lowering inequality while also putting growth-oriented policies into place to boost the economy. In view of this, there have been some developments that have taken place in the recent past. Some of them are mentioned below.
- On the FDI front, according to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), India's cumulative FDI inflow stood at Rs. 97,22,411 crore (US$ 1.09 trillion) between April 2000-June 2025; with major share coming from Singapore at Rs. 12,57,392 crore (US$ 142.88 billion) with a total share of 24%, followed by Mauritius at Rs. 11,10,692 crore (US$ 126.22 billion) with 21%, the USA at Rs. 5,41,654 crore (US$ 61.56 billion) with 10%, the Netherlands at Rs. 3,68,694 crore (US$ 41.90 billion) with 7%, and Japan at Rs. 2,88,090 crore (US$ 32.74 billion) with 6%.
- As on October 3, 2025, India’s foreign exchange reserves stood at Rs. 62,14,364 crore (US$ 701.24 billion).
- India registered 301 Private Equity (PE) deals worth Rs. 49,745 crore (US$ 5.7 billion) in Q3 2025, recording a 7% rise over the previous quarter. India-focused PE-VC funds raised Rs. 21,576 crore (US$ 2.47 billion) across 22 funds, a 148% YoY increase, driven by strong inflows into the IT & ITeS sector (US$ 2.4 billion). Mumbai led in investment value, while Bangalore topped in deal volume, reaffirming their positions as India’s leading investment hubs.
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have been net sellers in the Indian equity market since July, withdrawing over Rs. 1 lakh crore (US$ 11.36 billion) between July 1, 2025, and September 8, 2025, including Rs. 7,800 crore (US$ 886.4 million) in September, while in August 2025, Domestic Institutional Investors (DIIs) recorded their 25th straight month of net inflows, investing Rs. 94,829 crore (US$ 10.8 billion), the highest in 10 months. In the first five months of FY26, DIIs invested Rs. 3.24 lakh crore (US$ 37.6 billion), already 53% of the total investment made in FY25.
- India’s manufacturing sector strengthened further in August 2025, supported by firm demand that drove higher factory orders and production. Firms increased input purchases and hiring, backed by improved business confidence. Input inventories continued to rise and finished goods stocks expanded for the first time in nine months. The HSBC India Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) rose from 59.1 in July to 59.3 in August, marking the strongest improvement in operating conditions in over 17 years, with moderate cost pressures and a sharper rise in selling prices.
- India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI)-based inflation eased to an over eight-year low of 1.54% in September 2025, down from 2.05% in August 2025, driven by lower food and fuel prices, according to data from the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MOSPI).
- India’s GST collections reached an all-time high of Rs. 2.37 lakh crore (US$ 26.93 billion) in April 2025, rising 12.6% YoY. The growth was supported by strong domestic demand and higher imports, with domestic revenues up 10.7% and import revenues up 20.8%.
- Indian airlines carried over 1.36 crore passengers (13.6 million) in June 2025, marking an increase from the same period last year, as per official data.
- The government is focusing on renewable energy sources and has achieved a major clean energy milestone by generating 50% of its power from renewable sources, five years ahead of its 2030 target. India is committed to achieving the country's ambition of Net Zero Emissions by 2070 through a five-pronged strategy, ‘Panchamrit’. Moreover, India ranked 3rd in the renewable energy country attractive index.
- India secured 39th position out of 133 economies in the Global Innovation Index 2024. India rose from 81st position in 2015 to 39th position in 2024. India ranks 3rd position in the global number of scientific publications.
- In May 2025, the overall Index of Industrial Production (IIP) stood at 156.6 (base 2011–12 = 100), reflecting a YoY growth of 1.2%. The mining, manufacturing and electricity sectors stood at 136.6, 154.3 and 216 respectively.
- According to data released by the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI), India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) – Combined inflation was 3.34% in March 2025 against 4.85% in March 2024.
- India’s wheat procurement for FY26 has reached 29.7 million tonnes as of May 22, 2025, the highest in four years and up 13.5% YoY. Strong production of 115.43 million tonnes, favourable weather, and bonuses above the Minimum Support Price (MSP) in key states have driven this growth. The Food Corporation of India expects procurement to hit 32.5 million tonnes by season end, raising stocks to 44 million tonnes, well above the 18.4 million tonnes needed for the Public Distribution System.
Government Initiatives
Over the years, the Indian government has introduced many initiatives to strengthen the nation's economy. The Indian government has been effective in developing policies and programmes that are not only beneficial for citizens to improve their financial stability but also for the overall growth of the economy. Over recent decades, India's rapid economic growth has led to a substantial increase in its demand for exports. Besides this, a number of the government's flagship programmes, including Make in India, Start-up India, Digital India, the Smart City Mission, and the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation, is aimed at creating immense opportunities in India. In this regard, some of the initiatives taken by the government to improve the economic condition of the country are mentioned below:
- The Ministry of Labour & Employment signed an MoU with Zomato on October 14, 2025, to enhance employment opportunities through the National Career Service (NCS) portal. Under the agreement, Zomato will list around 2.5 lakh job opportunities annually, supporting the growth of the gig economy and promoting formal, technology-enabled livelihoods across India.
- In August 2025, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched two major agriculture schemes worth Rs. 35,440 crore (US$ 4 billion) - the PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana and the Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses aimed at boosting self-reliance, productivity, and farmers’ income. He also inaugurated and laid foundation stones for projects worth over Rs. 6,200 crore (US$ 709 million) across agriculture, animal husbandry, fisheries, and food processing sectors.
- On July 5, 2025, the Union Cabinet approved the Rs. 1,00,000 crore (US$ 11.72 billion) Research, Development and Innovation (RDI) Scheme, launching long‑term, low‑ or zero‑interest funding via a special purpose fund under the ANRF to jump‑start India’s R&D ecosystem and support deep‑tech and startup innovation.
- In March 2025, the Government announced several measures to boost industrial growth and investments, including initiatives such as Make in India, Start-up India, PM GatiShakti, and Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs also approved 12 new projects worth Rs. 28,602 crore (US$ 325.02 million) under the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP), spanning 10 states, to strengthen India’s manufacturing base and attract investments.
- On March 27, 2025, the Reserve Bank of India proposed doubling the investment cap for individual foreign investors in listed firms from 5% to 10%, with a combined foreign individual limit increasing to 24%, to counter Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) outflows.
- According to a report by Wood Mackenzie in January 2025, India, the United States, and West Asia are expected to collectively add 100 Gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity by 2025, while China is anticipated to continue its leadership in the solar industry.
- The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) and the Indian Ports Association (IPA) signed an MoU on December 24, 2024, to drive digital transformation in India’s maritime sector. The partnership focuses on system integration, software development, and use of emerging technologies to enhance efficiency and modernise port operations.
- In July 2024, the Ministry of Finance held the Union Budget and announced that for 2024-25, the total receipts other than borrowings and the total expenditure are estimated at Rs. 32.07 lakh crore (US$ 383.93 billion) and Rs. 48.21 lakh crore (US$ 577.16 billion), respectively.
- In February 2024, the Finance Ministry announced the total expenditure in Interim 2024-25 estimated at Rs. 47,65,768 crore (US$ 571.64 billion) of which total capital expenditure is Rs. 11,11,111 crore (US$ 133.27 billion).
- On January 22, 2024, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi announced the 'Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana'. Under this scheme, 1 crore households will receive rooftop solar installations.
- On September 17, 2023, Prime Minister Mr. Narendra Modi launched the Central Sector Scheme PM-VISHWAKARMA in New Delhi. The new scheme aims to provide recognition and comprehensive support to traditional artisans & craftsmen who work with their hands and basic tools. This initiative is designed to enhance the quality, scale, and reach of their products, as well as to integrate them with MSME value chains.
- On August 6, 2023, Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched to transform and revitalize 1309 railway stations across the nation. This scheme envisages development of stations on a continuous basis with a long-term vision.
- On June 28, 2023, the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change introduced the ‘Draft Carbon Credit Trading Scheme, 2023’.
- From April 1, 2023, Foreign Trade Policy 2023 was unveiled to create an enabling ecosystem to support the philosophy of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Local goes Global’.
- To enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities by increasing investment and production in the sector, the government of India has introduced the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for Pharmaceuticals.
- Prime Minister’s Development Initiative for North-East Region (PM-DevINE) was announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 with a financial outlay of Rs. 1,500 crore (US$ 182.35 million).
- Prime Minister Mr Narendra Modi has inaugurated a new food security scheme for providing free food grains to Antyodaya Ann Yojna (AAY) & Primary Household (PHH) beneficiaries, called Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Ann Yojana (PMGKAY) from January 1, 2023.
Road Ahead
India’s economy grew by 6.5% in FY25. With a 7.4% growth rate in Q4 FY25, the RBI has revised India's GDP growth forecast for FY26 upwards to 6.8% from earlier estimate of 6.5%.India's comparatively strong position in the external sector reflects the country's positive outlook for economic growth and rising employment rates. In 2024, India rose to 15th place globally in FDI rankings and retained its position as South Asia’s top recipient.
In H1 FY25, India’s growth-focused approach was underscored by the government’s capital expenditure outlay of Rs. 15,02,000 crore (US$ 176 billion), reinforcing its commitment to infrastructure-led development. In the Union Budget of FY26, capital expenditure took lead by steeply increasing the capital expenditure outlay by 10% to Rs. 11,21,000 crore (US$ 131 billion) over Rs. 10,18,000 crore (US$ 119 billion) in FY25. Stronger revenue generation because of improved tax compliance, increased profitability of the company, and increasing economic activity also contributed to rising capital spending levels.
India’s total goods and service exports surged by 76% over the past decade, touching Rs. 70,36,425 crore (US$ 825 billion) in FY25, driven by strong performance in engineering goods, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. With a reduction in port congestion, supply networks are being restored. With a proactive set of administrative actions by the

government, flexible monetary policy, and a softening of global commodity prices and supply-chain bottlenecks, inflationary pressures in India look to be on the decline overall.




