Tripura
Tripura is the second largest natural rubber producer in the country.
Introduction

Tripura, one of the northeast states, share borders on the north, west, south, and southeast by Bangladesh, and in the east, it shares border with Assam and Mizoram.
The state has favourable climatic conditions for cultivation of various fruit and horticultural crops. It is rich in natural resources such as natural gas, rubber, tea, and medicinal plants.
Tripura holds a strong tea plantation base in India, with 54 tea gardens covering an area of 12,832 hectares, as of June 2025.
The state is also rich in natural gas deposits, glass sands, limestone, plastic clay, and hard rock. With its pleasant climate and scenic landscape, Tripura is a favoured tourist destination. The state offers tourist attractions such as historical Hindu and Buddhist sites, temples, rivers, and rock carvings. In 2019, the number of foreign tourist arrivals in the state was recorded to be 154,405.
The state has favourable climatic conditions for cultivating various fruit and horticultural crops including rice, jackfruit, pineapple, potato, sugarcane, chilli, and
natural rubber. Rice is the major crop of the state and is cultivated in 91% of the cropped area. The state has a wide variety of medical plants having 266 medicinal plants, 379 species of trees, 581 herbs, 320 shrubs and 165 climbers.
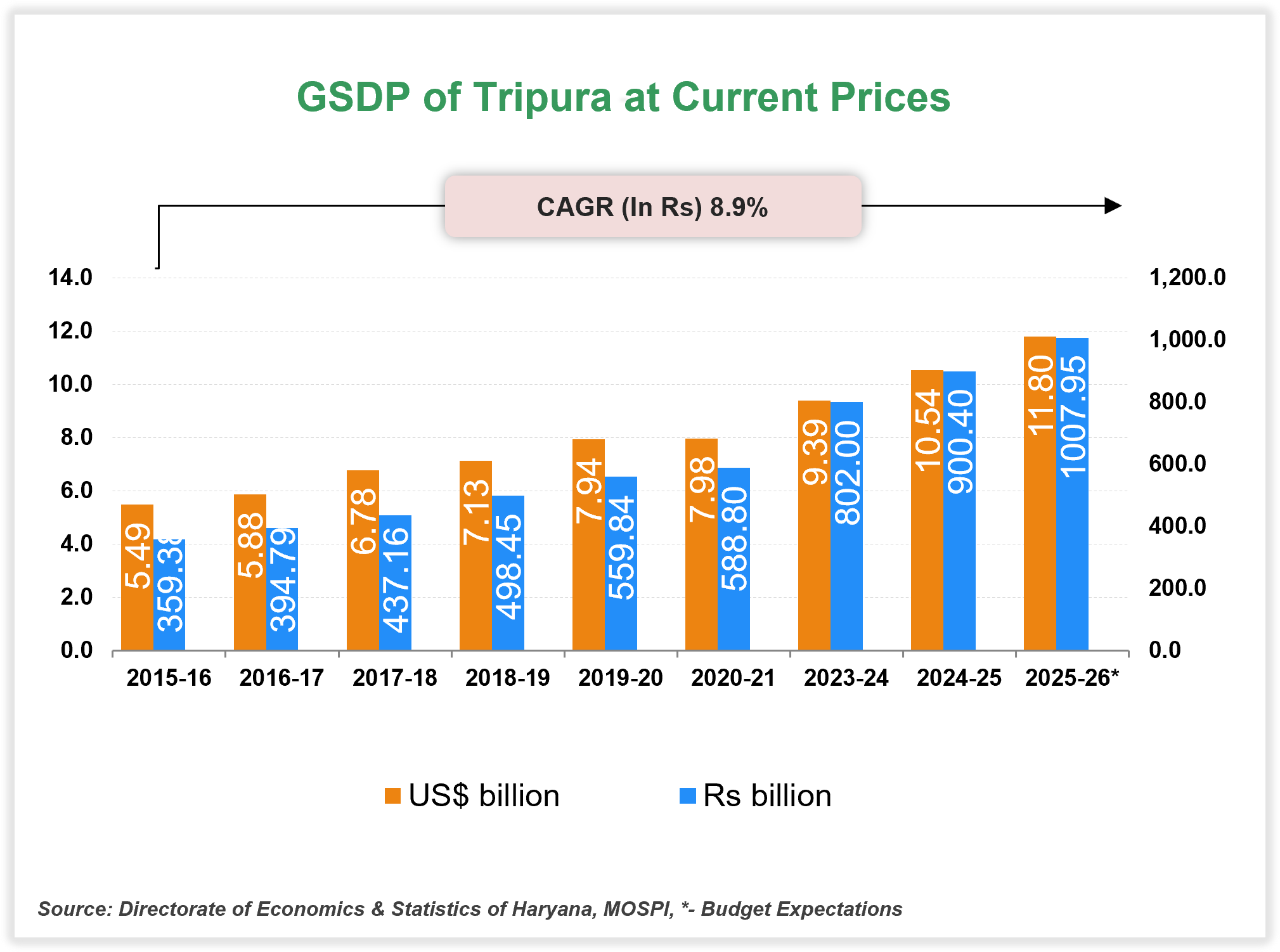
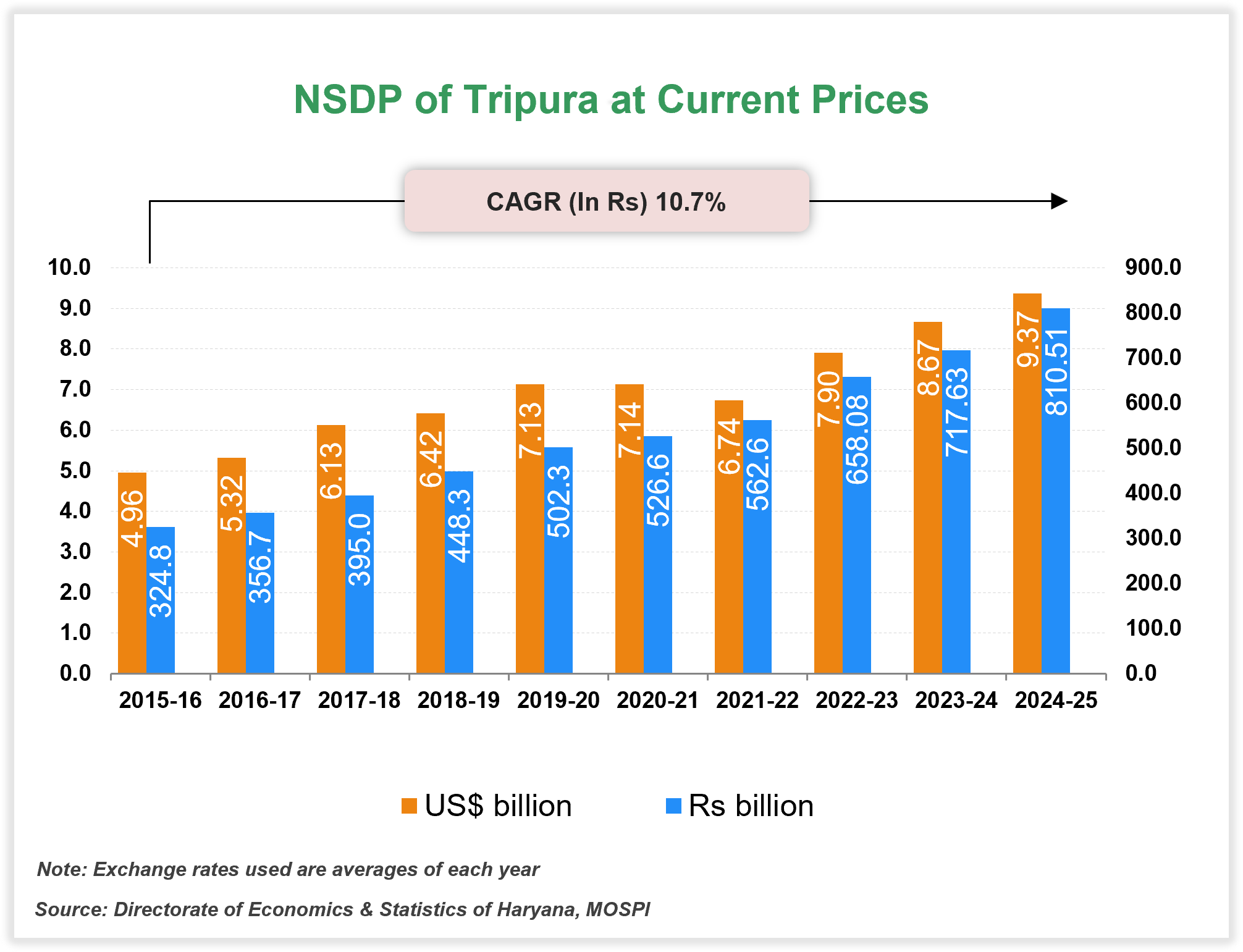
At current prices, Tripura’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) stood at Rs. 1,007.95 billion (US$ 11.80 billion) in FY26. GSDP increased at a CAGR of 8.9% between FY16 and FY26.
According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), between October 2019-June 2025, FDI inflow in Tripura stood at Rs. 9.75 crore (US$ 1.23 million).
Total merchandise exports from the state stood at Rs. 105 crore (US$ 12. 13 million) in FY25.
Tripura exported key items such as engineering goods, spices, drugs and pharmaceuticals, and organic and inorganic chemicals
Tripura has 93.7% literacy rate, higher than the national average rate, making it an ideal destination for knowledge sectors.
As of August 2025, Tripura had a total installed power generation capacity of 656.98 MW, of which 121.01 MW was under state utilities, 511.68 MW was under central utilities and 24.29 MW was under the private sector.
Of the total installed capacity, 542.94 MW was contributed by thermal power, 68.49 MW by hydropower and 45.55 MW by renewable resources, as of August 2025.
According to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Tripura had 3.28 million wireless and 0.05 million wireline subscribers, as of March 2025.
Tripura had a total tele-density of 78.78%, as of March 2025.
The number of internet subscribers in Tripura stood at 2.19 million, as of March 2025.
The state has a wide range of fiscal and policy incentives for businesses under the Tripura Industrial Investment Promotion Incentive Scheme, 2017. Developing infrastructure, improved rail and air connectivity, and establishment of trade routes have facilitated trade.
Key Sectors
- In August 2025, Tripura’s Chief Minister approved Rs. 87 crore (US$ 9.97 million) for infrastructure upgrades, including Rs. 32.33 crore (US$ 3.7 million) for Agartala roads and drains and Rs. 55.16 crore (US$ 6.32 million) for maintaining 129.5 km of PMGSY roads.
- Tripura has crossed the 4 MW mark in rooftop solar generation, with over 1,200 homes installed under the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana.
- In the State Budget FY26, the allocation for urban development is Rs. 1,041 crore (US$ 121.9 million).
- Under the State Budget FY26, Rs. 3,948 crore (US$ 462.1 million) has been allocated to the education, sports, and art & culture sector.
- Under the State Budget FY26, Rs. 1,890 crore (US$ 221.2 million) has been allocated to the health and family welfare.
- Under the State Budget FY26, Rs. 1,945 crore (US$ 227.7 million) has been allocated to agriculture and allied industries.
- The agro-climatic conditions in the state are favourable for growing various fruits and horticultural crops. Tripura’s pineapples and oranges are known for their unique flavour and organic nature.
- As per the third advance estimate of 2023-24, the total fruit production in the state is 617.55 thousand MT, vegetables are 1147.71 thousand MT, plantation is 45.71 thousand MT and spices are 26.50 thousand MT.
- Tripura has developed a horticulture action plan for 2020-21, with estimated capital outlay of Rs. 123.54 crore (US$177 million). The main objective of this annual plan is to increase the production and productivity of various horticulture crops in the state
- Tripura has vast natural gas reserves. The gas is available in a non-associate form, with high methane content of about 97.0%. Concessional gas-pricing and vast reserves offer potential for setting up industries in the sector. Natural Gas production in Tripura stood at 1,531 million cubic metres (mcm) during 2021-22.
- Tea grown in Tripura is known for its good blending qualities. Organic tea and green tea production have been undertaken by some of the tea estates in the state. Tea production is a growing industry in Tripura and provides a considerable scope for investment.
Tripura, a northeastern state bordering Bangladesh on three sides and Assam and Mizoram to the east, offers strong agro-based and resource-driven opportunities. The state benefits from fertile agro-climatic conditions supporting rice, fruits, horticulture, rubber, spices and tea, with 54 tea gardens spread over 12,832 hectares. Rich reserves of natural gas, limestone and medicinal plants underpin industrial potential, while tourism is supported by scenic landscapes and heritage sites. With a high literacy rate of 93.7%, improving road, rail and air connectivity, reliable power capacity of 656.98 MW, and policy support under the Industrial Investment Promotion Incentive Scheme, the state presents a conducive environment for investment across agriculture, energy, tourism and manufacturing sectors.




