Nagaland
Nagaland’s estimated hydropower generation potential stood at 1,452 MW and the overall installed hydro capacity stood at 66.33 MW in May 2024, presenting huge investment opportunities in the state.
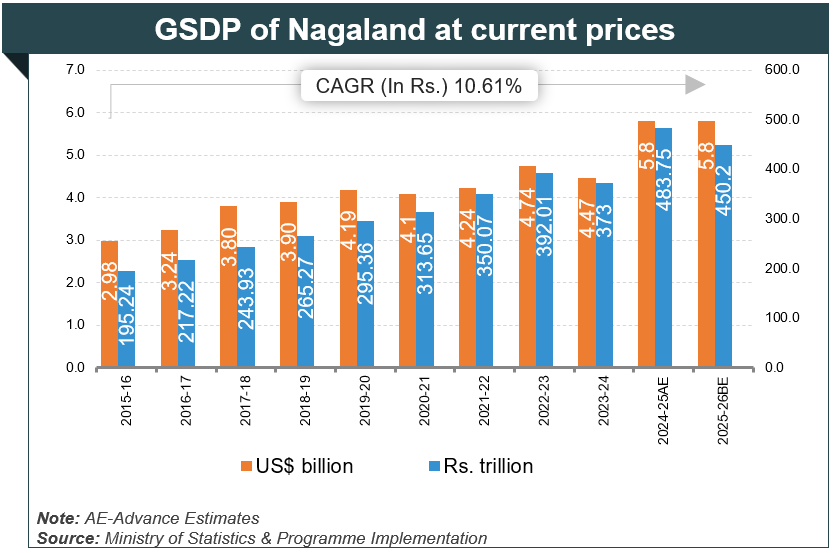
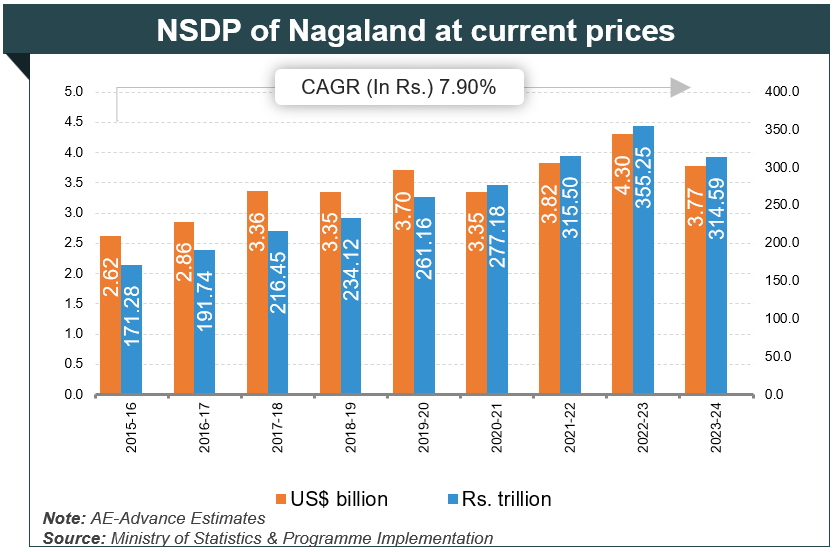
Introduction

Nagaland is one of the seven northeast states and is located on India’s farthest east side. The state is flanked by Myanmar in the east, Arunachal Pradesh in the north, Assam in the west, and Manipur in the south.
The state has considerable resources of natural minerals, petroleum, and hydropower. It has unexploited reserves of around 600 million metric tonnes (MT) of crude oil and more than 20 MT of hydrocarbons. Moreover, the state has 315 MT of coal reserves and 1,038 MT of limestone reserves. The agro-climatic conditions in Nagaland provide multiple commercial opportunities for floriculture and horticulture. The state has 650 indigenous species of medicinal and aromatic plants. Bamboo is found extensively in Nagaland, with bamboo growing stock covering nearly 5% of the total stock in the country. As of 2019, Nagaland had 46 species of bamboo. Raw silk production in the state stood at 264 MT in 2020-21, 273 MT in 2021-22 and 304 MT in 2022-23, 399 MT in 2023-24.
As of September 2025, Nagaland has a total installed power generation capacity of 208.20 MW, of which 172.36 MW was under the central sector, 32.67 GW under state utilities, and 3.17 GW under the private sector.
Out of the total installed power generation capacity, 106.03 MW was contributed by thermal, 66.33 MW by hydro, and 35.84 MW by renewable energy.
Total exports from Nagaland in FY25 stood at Rs. 14 crore (US$ 1.60 million).
Major items exported from Nagaland in FY25 are Minerals, cotton yarns and handicrafts.
The state provides institutional support through various central and state government agencies viz., the North East Council, the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region and the Nagaland Industrial Development Council.
The state offers excellent policy and fiscal incentives for agro-based and forest-based industries, horticulture, food processing, mining, tourism, and the handloom and handicraft sectors. Industrial centres and special economic zones (SEZs) are being developed to enhance the marketability of products.
According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), FDI inflows to Nagaland totalled Rs. 0.52 crore (US$ 0.06 million) between October 2019-June 2025.
Recent Developments in Key Sectors
- In September 2025, Medanta, in partnership with IDAN and the Nagaland Government, launched “A Guide to Better Health” to promote preventive healthcare and wellness. The initiative, unveiled by Chief Minister Mr. Neiphiu Rio, was followed by a three-day medical camp in Kohima benefiting over 400 people.
- In September 2025, the Government of Nagaland signed an MoU with the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) to strengthen the state’s public healthcare system through innovative indigenous health technologies. The partnership aims to develop sustainable, locally relevant healthcare solutions, enhance medical infrastructure, and promote research-driven innovations for improved health outcomes across Nagaland.
- The first-ever inward freight rake arrived at Molvom station in Nagaland on September 24, 2025, carrying 41 wagons of cement from Telangana. The first outward rake was dispatched from Molvom to Jirania on September 29, 2025, with 42 wagons of stone chips, marking the beginning of freight operations from Nagaland.
- In August 2025, Chief Minister of Nagaland, Mr. Neiphiu Rio virtually inaugurated 51 school infrastructure projects across Nagaland under the Samagra Shiksha scheme, including new school buildings, classrooms, teachers’ quarters, and a hostel, marking a key step in upgrading the state’s education facilities.
- As of August 2025, 37 households in Nagaland have been benefited under the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, with 584 applications submitted on the national portal.
- In April 2025, Sakra World Hospital, Bengaluru, signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Nagaland Health Protection Society, registered under the State Government of Nagaland. The move aims to enhance the well-being of accessible medical services for government employees, pensioners, and Indigenous Inhabitants or Permanent Residents of Nagaland under the Chief Minister Health Insurance Scheme (CMHIS-EP).
- On November 30, 2024, the Government of Nagaland, in collaboration with the British High Commission and the Welsh Government, hosted a significant roundtable discussion at Hotel Vivor in Kohima. This event aimed to showcase Nagaland's investment potential and foster international partnerships in sectors such as agritech, creative economy and entrepreneurship. The Roundtable concluded with a shared vision for fostering innovation, cultural exchange and economic development through enduring partnerships.
- On December 2, 2024, a roundtable discussion took place at Bamboo Hall, Kisama. This event brought together representatives from partner countries; Peru and partner states - Sikkim and Telangana—to explore avenues for cultural exchange, tourism promotion and economic collaboration. Discussions focused on leveraging cultural heritage and tourism to drive economic growth and strengthen ties between the participating regions.
- The Government of Nagaland and the British High Commission to India signed a landmark Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on November 30, 2024, to reserve five annual slots in the prestigious Chevening Scholarship program exclusively for candidates from Nagaland. Under this agreement, the Government of Nagaland will part-fund the reserved slots, enabling aspiring leaders from the state to pursue fully funded one-year master's degrees at any UK university of their choice.
- An MoU between Salesforce.com Private Limited and Directorate of Higher and Technical Education was signed on December 2, 2024, for creating a new talent in the Salesforce ecosystem by enabling students on Salesforce skills by helping students to build digital fluency, give them opportunity to skill/up-skilled and also get deep skilled to be Salesforce career ready students.
- The Investment and Development Authority of Nagaland (IDAN) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Omsheel Group Private Limited on December 2, 2024. This agreement focuses on fostering collaboration in the agritech sector, aiming to enhance agricultural practices and promote sustainable development within the State. The partnership between IDAN and Omsheel Group is expected to introduce innovative agricultural technologies and practices to Nagaland, thereby improving productivity and contributing to the State's economic growth.
- The State Government has given the clearance for a 21 MW hydropower project at Hakchang village in Tuensang district and a 27 MW thermal project at Tuli, both of which are expected to be operational during 2022-23.
- On October 14, 2023, Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya inaugurated Nagaland's first medical college, NIMSR, in Kohima, offering 100 MBBS seats with 85 reserved for state students and 15 for students nationwide, emphasizing research, international opportunities, and healthcare accessibility initiatives.
- On March 19, 2024, Construction activities have commenced at Portal 1 of Tunnel number 7 of the Dimapur-Kohima new rail line project in Tsiepama village, marking the beginning of the construction of the longest tunnel in the entire rail line.
- In June 2023, IIM Shillong signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Government of Nagaland for providing accessible and quality education to the students of Nagaland.
- In June 2023, 250 farmers in Nagaland received user authorization for two agricultural products, Naga tree tomato and Naga cucumber, allowing them to use Geographical Indication (GI) for these items.
- In March 2023, Union Minister for Roads, Transport and Highways, Mr. Nitin Gadkari informed that the government is constructing a 14.71 kilometre-long four-lane highway from Dimapur to Kohima (Package-II) in Nagaland, costing Rs. 339.55 crore (US$ 41.1 million).
- In January 2023, Google Cloud and non-government organisation eGovernment Foundation, along with the government of Nagaland unveiled the TeleICU Hub at the Naga Hospital Authority, Kohima. The facility was aimed to transform secondary care management and bridge gaps in critical health services.
- In March 2022, the Nagaland Government signed a power purchase agreement (PPA) with Hyderabad-based Halo Energie Pvt Ltd to develop Nagaland’s first greenfield solar power project in Dimapur. The 20 MW power project is estimated to cost around Rs. 120 crore (US$ 15.7 million) and generate 28 million units per year.
- In a recent development in August 2022, Nagaland got its second railway station after a gap of more than 100 years with the commissioning of a new facility at Shokhuvi. Dimapur Railway Station, which is situated in the heart of the commercial hub of the state.
- The Central government allocated Rs. 145 crore (US$ 17.5 million) to Nagaland for the construction of a Unity Mall in Dimapur. This funding is part of the Union Budget 2023-24, which has set aside Rs. 5,000 crore (US$ 605.2 million) for the establishment of Unity Malls across the country. The mall in Nagaland aims to promote and showcase the state’s One District One Product (ODOP) offerings, highlighting the unique products and industries of the region.
Nagaland, located in India’s far eastern Northeast, borders Myanmar, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam and Manipur, and is rich in natural resources including crude oil, hydrocarbons, coal, limestone and hydropower. The state has strong agro-climatic advantages for horticulture, floriculture and medicinal plants, with extensive bamboo resources and a steadily growing sericulture sector. As of September 2025, Nagaland’s installed power capacity stood at over 200 MW, led by thermal, hydro and renewable sources. Exports remain modest, led by minerals, cotton yarn and handicrafts. The state offers attractive policy and fiscal incentives for agro-based, forest-based, mining, tourism, handloom and handicraft industries, supported by agencies such as the Northeast Council and IDAN. Recent developments include new freight rail operations, healthcare partnerships, education and skilling initiatives, renewable energy projects, and expanding road and rail connectivity, strengthening Nagaland’s investment and growth potential.
Note: MW - Megawatt




