Uttarakhand
Under the Vision 2030, the processing capacity of horticulture produce will be enhanced from 7.5% to 15% of the total horticulture production by 2030.

Introduction

Uttarakhand is in the foothills of the Himalayan Mountain range. The state shares borders with China (Tibet) in the north, Nepal in the east, and inter-state boundaries with Himachal Pradesh in the west and northwest and Uttar Pradesh in the south. It has almost all agro-geo climatic zones, which provide commercial opportunities for floriculture and horticulture. The state is home to more than 175 species of rare medicinal, aromatic & herbal plants. The state has proximity to the national capital, Delhi, a leading market of the country and excellent connectivity with neighbouring states. Uttarakhand has abundant natural resources due to hills and forests. Its agro-climatic conditions support horticulture-based industries. The vast water resources available in the state are also favourable for hydropower.
Uttarakhand is one of the fastest growing states in India, thanks to the massive growth in capital investment arising from conducive industrial policy and generous tax benefits.
The state offers a wide range of benefits in terms of interest incentives, financial assistance, subsidies, and concessions. Uttarakhand has a robust social and industrial infrastructure, virtual connectivity with over 39,000 km of road network, two domestic airports, and 345.23 km of rail routes.
Uttarakhand Tourism
Uttarakhand aims to double tourist inflow to 70 million by 2030, strengthening its tourism sector through fiscal incentives such as reducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) on hotel tariffs up to Rs. 7,500 (US$ 85.07) from 12% to 5%, making travel more affordable across key destinations including Nainital, Mussoorie, Auli, Haridwar, Rishikesh and Chopta. On October 24, 2025, the State launched the Rs. 18,520 crore (US$ 2.11 billion) Sharda Corridor Project to boost tourism, connectivity and local economic growth, alongside major ropeway initiatives such as the 13 km Sonprayag-Gaurikund-Kedarnath ropeway worth Rs. 985 crore (US$ 126.77 million) and two additional ropeways in Mussoorie and Yamunotri by Empyrean Skyview Projects with an investment of Rs. 700 crore (US$ 90.09 million).
The launch of www.uttarastays.com, a state-sponsored homestay portal featuring around 5,000 listings, further promotes community-based tourism, supports nearly 80,000 livelihoods, and enhances the linkage with local cottage industries and traditional crafts.
The economy of Uttarakhand
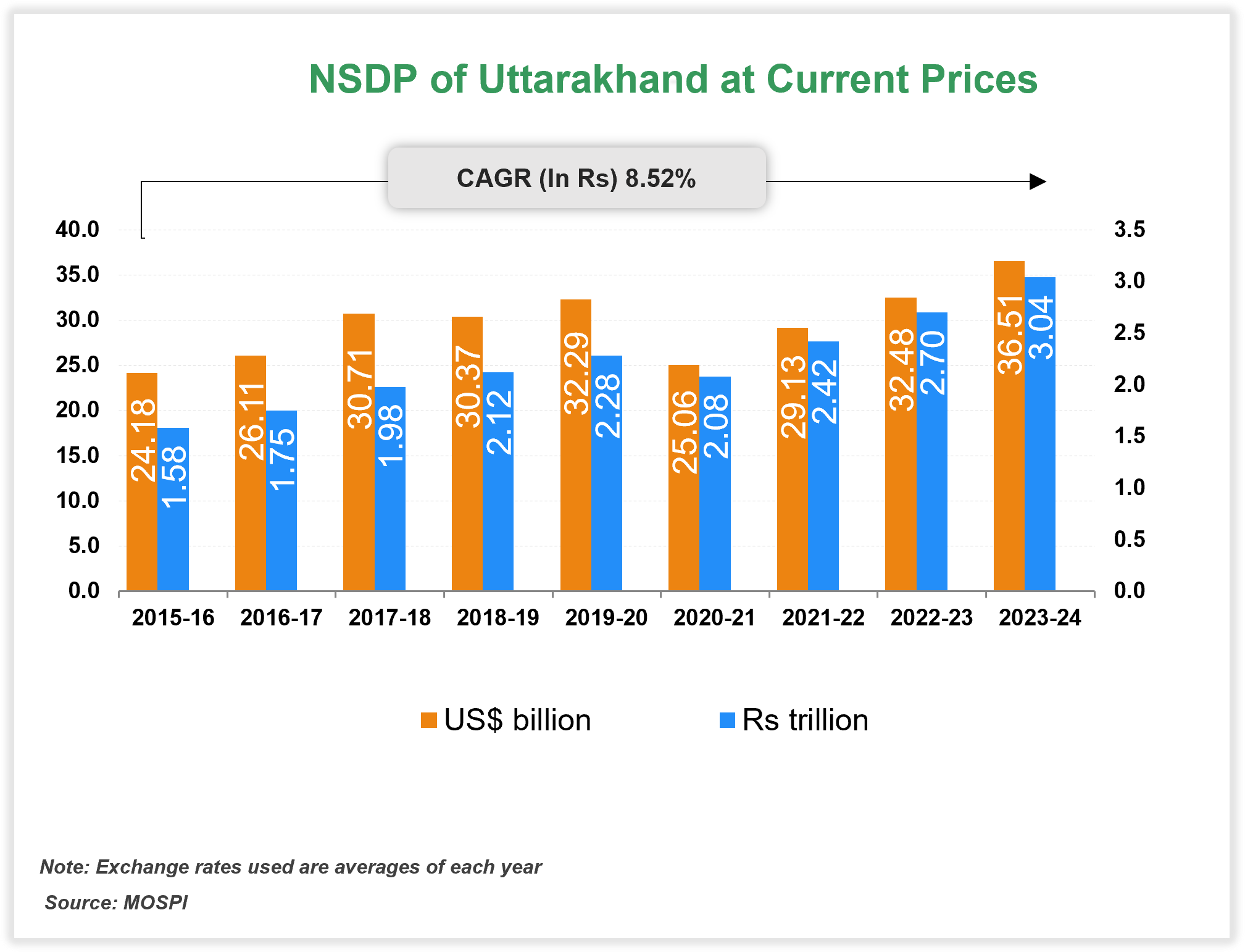
At current prices, Uttarakhand’s GSDP is projected to be Rs. 4.29 trillion (US$ 50.26 billion) in FY26. Between FY19 and FY26, GSDP of the state is estimated to increase at a CAGR of 8.86%. According to Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), between October 2019-June 2025, FDI inflow in Uttarakhand stood at Rs. 28,965 crore (US$ 3.26 billion). Major items exported from Uttarakhand are Engineering Goods and Drugs and Pharmaceuticals, Electronic Goods, Plastic and Linoleum, etc.
Industries in Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand is one of the fastest growing states in India, thanks to the massive growth in capital investment arising from conducive industrial policy and generous tax benefits. The MSME sector plays a crucial role in the economic and social development of the state as this sector is the nursery of entrepreneurship. The government has placed a special mandate in its Vision 2030 strategy to develop the MSME sector. In the State Budget 2024-25, crop husbandry has been allocated Rs. 644 crore (US$ 77.25 million) which includes schemes such as National Mission for Natural Farming and PMKSY. Additionally, Rs. 157 crore (US$ 18.83 million) is allocated for research assistance to agriculture institutions. As part of the State Budget 2023-24, over the next three years, 50,000 polyhouses (a type of greenhouse) will be set up to promote cluster-based horticulture. Six ‘aroma valleys’ will also be developed, such as the Cinnamon Valley in Nainital and Mint Valley in Haridwar.
Recent Developments in Key Sectors
- On October 24, 2025, the Uttarakhand Government launched the Rs. 18,520 crore (US$ 2.11 billion) Sharda Corridor Project to enhance tourism, connectivity, and local economic growth. The project aims to develop border villages as cultural and religious hubs, boost infrastructure in the Sharda Peeth region, and promote sustainable tourism while improving livelihoods in remote areas.
- On October 17, 2025, the Uttarakhand government, in collaboration with the India AI Mission and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, hosted the Uttarakhand AI Impact Summit 2025 as a pre-summit event to the India AI Impact Summit 2026. The summit emphasised responsible, inclusive AI growth and pledged to make world-class computing power accessible at less than a dollar an hour.
- In October 2025, the Uttarakhand Education Department launched a free coaching initiative for over 10,000 students from economically weaker sections across Arts, Science and Commerce streams to improve competitive exam preparedness and promote education equity.
- In August 2025, Maya Devi University in Dehradun was recognised as an emerging innovation-driven global education hub, offering advanced digital programmes, strong industry linkages, and scholarships to promote inclusive and technology-focused learning.
- In August 2025, the Government of India has sanctioned Rs. 547.8 crore (US$ 62.4 million) for power infrastructure modernisation in Rishikesh and Dehradun in Uttarakhand. In Rishikesh, the funds will facilitate underground cabling to enhance safety and reduce outages. In Dehradun, deployment of a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system will enable real-time grid monitoring and smarter load management. These upgrades support the state’s aim of delivering reliable, resilient and future-ready electrical services.
- In August 2025, the Uttarakhand government launched multiple Information and Communication Technology (ICT) services including the “Digital Uttarakhand App”, 66 new websites under the S3WaaS platform, a GIS-based rubbish-truck tracking system, an AI-enabled CM Helpline (1905) and an encroachment-monitoring web app to enhance transparency, speed and citizen access.
- On March 8, 2025, the Uttarakhand government announced a push for horticulture and floriculture, highlighting state efforts to scale up high-value flower farming (including tulips), provide technical support and market linkages for growers, and harness the Himalayan climate to make the State a major floriculture hub.
- Under GST 2.0, the Government of India has reduced the GST rate on Uttarakhand’s key hill produce, including Pahari Toor Dal, Uttarakhand Red Rice, and Lakhori Mirchi, from 12% to 5% to boost local agriculture and farmer incomes. The move is expected to benefit nearly 9,000 farmers across the State and promote sustainable, organic farming practices rooted in traditional systems such as Barahnaja.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), has sanctioned the development of a 12.4 km ropeway project connecting Govindghat to Hemkund Sahib Ji in Uttarakhand. This initiative will be executed under the Design, Build, Finance, Operate, and Transfer (DBFOT) model, with a total capital investment of Rs. 2,730 crore (US$ 319.9 million).
- Uttarakhand Tourism has launched www.uttarastays.com, a state-sponsored homestay booking portal that allows nearly 5,000 homestay owners to list their properties for free, promoting local tourism and providing training to enhance customer service skills.
- The Uttarakhand government signed investment MoUs worth Rs. 4,600 crore (US$ 551.43 million) with various companies, including those in the agro-industry such as Himalayan Basket and Silage Agro, during a roadshow in Bengaluru, highlighting the state's focus on food processing and agricultural development.
- The Centre has allocated Rs. 559 crore (US$ 67.01 million) for 33 infrastructure projects in Uttarakhand, including funds for a tunnel parking facility at Kempty Fall, an inter-state bus terminal in Herbertpur, and health infrastructure improvements at Haridwar Medical College, as part of the 'Scheme for special assistance to states for capital investment 2023-24’.
- Union Defence Minister Mr. Rajnath Singh inaugurated 35 infrastructure projects worth Rs. 670 crore (US$ 80.32 million) in Joshimath, Uttarakhand, including roads and bridges across seven states, emphasizing the importance of timely completion, national security, and environmental considerations in border area development.
- As of June 2024, the state had a total installed power generation capacity of 4,459.48 MW. Of this, hydro power accounted for 2,155.89 MW, followed by thermal power at 1,335.76 MW, renewable power at 936.59 MW, nuclear power at 31.24 MW.
- In the State Budget FY26,
- In FY26, a total of 220 kilometres of new roads is planned to be constructed, while 1,500 kilometres of existing roads will undergo renovation, and 1,000 kilometres will be reconstructed.
- A capital outlay of Rs. 1,202 crore (US$ 140.7 million) has been designated for power projects.
- Rs. 3,618 crore (US$ 423.6 million) has been allocated to government primary schools
- Rs. 4,014 crore (US$ 470.0 million) revenue expenditure is budgeted for government secondary schools.
- Uttarakhand has allocated Rs 1,662 crore (US$194.6 million) has been allocated towards allopathic rural health services and Rs. 927 crore (US$ 108 million) towards allopathic urban health services.
- Rs. 688 crore (US$ 80.6 million) has been allocated towards horticulture and vegetable crops.
- With the establishment of the Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) earth station at Dehradun, Uttarakhand now offers high-speed connectivity.
- Information Technology is an enabling sector that provides underpinning of smooth connectivity throughout the state in various departments, businesses, and homes, thereby improving productivity and efficiency across sectors. Given the high literacy rate of 78.82% in the state, employment opportunities for educated youth can be generated by encouraging ICT, ITES and electronics manufacturing units to establish their enterprises in Uttarakhand.
- Uttarakhand Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship was launched in 2018, which aims to increase the employability of workers, competitiveness of enterprise, and inclusiveness of growth.
- Under the State’s Vision 2030, the processing capacity of horticulture produce will be enhanced from 7.5% to 15% of the total horticulture production by 2030.
- The MSME sector envisages massive expansion in the future, which would increase employment from the existing 2.58 lakh people to 8.5 lakh people by 2030.
- Sonprayag-Gaurikund-Kedarnath ropeway project undertaken by National Highways Logistics Management Limited (NHLML) will be 13 km in length and the estimated cost of the project will be over Rs. 985 crore (US$ 126.77 million).
- Empyrean Skyview Projects will develop two more ropeway systems in Mussoorie and Yamunotri with an investment of Rs. 700 crore (US$ 90.09 million)




