Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh earned record revenue of Rs. 12,941 crore (US$ 1.57 billion) from minerals for the year 2022-23 and accounted for more than 17% of total mineral production in India.
Introduction

Chhattisgarh is in the central part of India. The state shares its border with Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in the west, Uttar Pradesh in the north, Odisha and Jharkhand in the east, and Andhra Pradesh in the south.
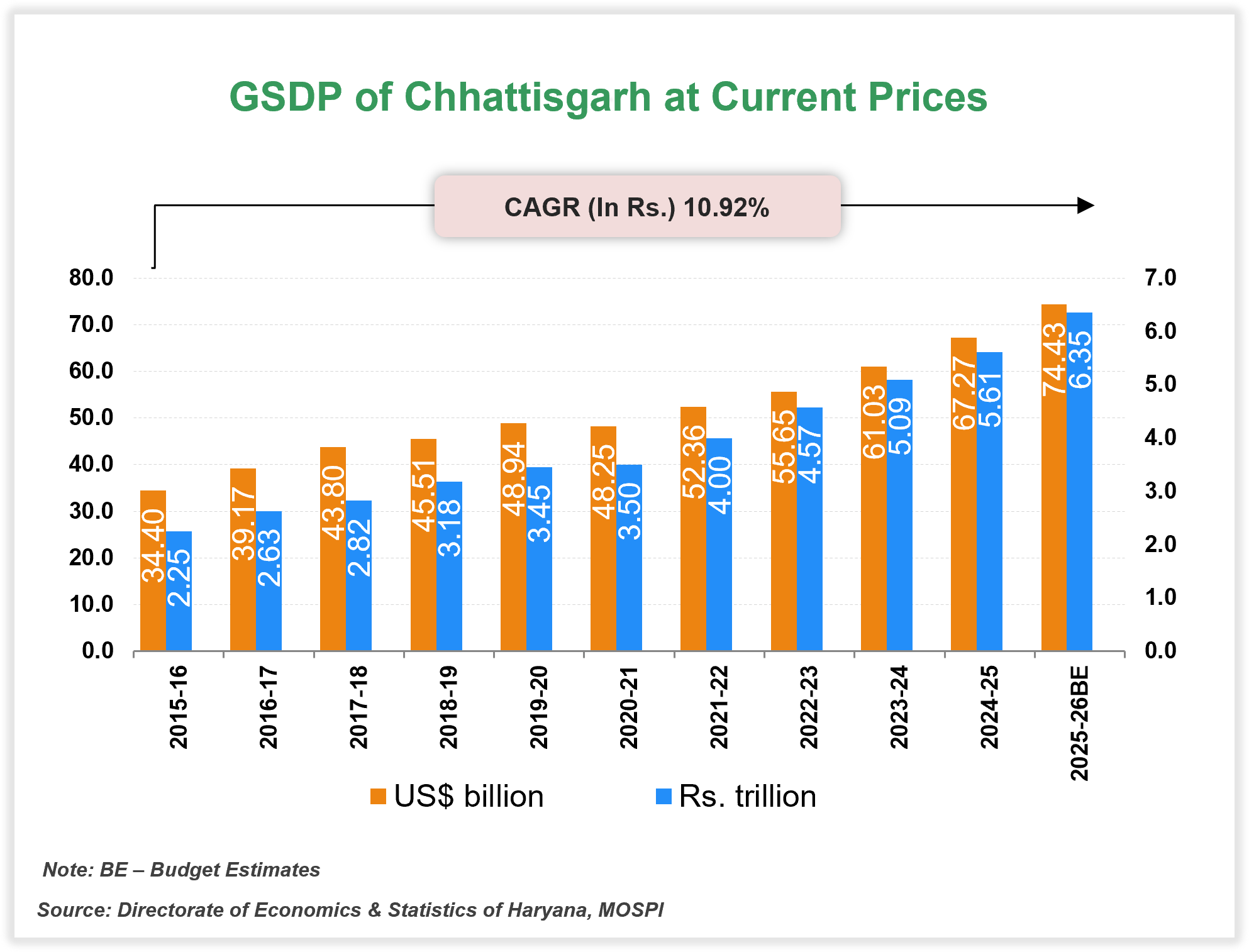
At current prices, the total GSDP of Chhattisgarh was estimated to reach Rs. 6.35 trillion (US$ 74.43 billion) in FY26. The state’s GSDP (in Rs.) increased at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.92% from FY16 to FY26.
Chhattisgarh is presently one of the few states that have surplus power. Korba district in Chhattisgarh is known as the power capital of India. It is also among the few profitable states in terms of utility-based electricity. As of September 2025, Chhattisgarh had a total installed power generation capacity of 15,036.40 MW, comprising 10,036.53 MW under private utilities, 1,995.95 MW under state utilities, and 3,003.92 MW under central utilities.
Mineral resources are Chhattisgarh's biggest strength. It is a leading producer of minerals such as coal, iron ore and dolomite. Moreover, considerable reserves of bauxite, limestone and quartzite are available in the state. The state accounts for 35.4%
of tin ore reserves of India. Chhattisgarh is the only state in India that produces tin concentrates.
Chhattisgarh has emerged as one of the most preferred investment destinations in India. According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), FDI inflow to the state totalled Rs. 1,238 crore (US$ 139.63 million) from October 2019-June 2025.
According to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Chhattisgarh had 22 million wireless and 0.33 million wireline subscribers as of June 2025. Tele-density in Chhattisgarh stood at 72.09% in this period.
In FY26 (April-August 2025), Chhattisgarh accounted for 13.1% of the total value of mineral production in India.
Total merchandise exports from Chhattisgarh stood at Rs. 19,421 crore (US$ 2.19 billion) in FY25. Rice, iron ore, electronic goods and engineering goods were the main export products contributing to the state’s merchandise exports.
On October 1, 2024, the Centre approved Rs. 11,000 crore (US$ 1.32 billion) for the development of four major national highways in Chhattisgarh, with Union Minister Mr. Nitin Gadkari directing the forest department to expedite clearances and resolve project delays, aiming to enhance the state's infrastructure and support industrial growth.
In the last 25 years the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) has delivered approximately 40,415 km of rural roads in Chhattisgarh, transforming connectivity (including 12,459 km in Left-Wing-Extremism affected zones) and linking 3,853 previously isolated habitations.
The Chhattisgarh state has secured the largest allocation from the Indian Railways infrastructure push announced on April 4, 2025, with Rs. 8,741 crore (US$ 1 billion) approved for a new 615 km railway line connecting Kharsia to Naya Raipur via Parmalakasa.
A wide range of fiscal and policy incentives for businesses were announced under its Industrial Policy, 2014-19. Additionally, the state has well-drafted policies for the IT/ITeS, solar energy, agro and food processing, minerals and biotechnology sectors. Chhattisgarh stands fourth among Indian states in rankings based on ease of doing business and reform implementation, according to a study by the World Bank and KPMG.
On October 16, 2025, the State of Chhattisgarh was adjudged the best-performing state under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), thanks to its exemplary transparency, near-zero pendency of claims and effective implementation of the scheme. The award recognises the state’s commitment to efficient public-health service delivery and accountable governance.
Key Sectors
- In FY26 (April-August 2025), the limestone production in the state stood at 20.17 million tonnes.
- On November 4, 2025, the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) facilitated the first export of 12 metric tonnes of Fortified Rice Kernel (FRK) from the State of Chhattisgarh to Costa Rica. This milestone aligns with the vision of the Poshan Abhiyan (Nutrition Mission) under the Narendra Modi government to combat malnutrition. The export highlights Chhattisgarh’s growing role in nutrition-focused value chains and India’s increasing presence in global food markets.
- On October 7, 2025, the State of Chhattisgarh launched a women-friendly electric tractor pilot at Indira Gandhi Krishi Vishwavidyalaya (IGKV) in Raipur. The initiative aims to promote green and inclusive farming by introducing low-emission, user-friendly mechanisation designed especially for women farmers.
- Allotment under the State Budget FY26
- Rs. 7,186 crore (US$ 842.3 million) was allocated for roads and bridges.
- Rs. 947 crore (US$ 111.0 million) has been allocated towards Naya Raipur Atal Nagar Vikas Pradhikaran
- Rs. 5,394 crore (US$ 632.3 million) has been allocated for higher secondary schools and Rs. 5,859 crore (US$ 686.8 million) has been allocated for Government primary schools.
- Rs. 1,850 crore (US$ 216.9 million) has been allocated towards the National health mission and Rs. 1,500 crore (US$ 175.8 million) has been allocated towards shahid veernarayan singh ayushman swasthya yojana.
- Rs. 23,357 crore (US$ 2.80 billion) was allocated towards agriculture and allied industries, out of which Rs. 10,000 crore (US$ 1.20 billion) was allocated towards the Krushak Unnati Yojana.
- Apparel: Chhattisgarh is one of the leading producers of tussar and kosa silks in the country and has the potential to be a strong player in the Indian apparel industry. Raw silk production in the state reached 349 metric tonnes in 2018-19, 480 metric tonnes in 2019-20, 224 metric tonnes in FY22, and 223 metric tonnes in FY23.
Chhattisgarh offers a compelling growth and investment landscape, underpinned by strong GSDP expansion, surplus power availability, and a rich mineral base. Robust infrastructure development across roads, railways, and highways, along with policy-driven ease of doing business, is strengthening industrial competitiveness. Rising exports, leadership in mining and power generation, and focused investments in agriculture, healthcare, and human development are supporting inclusive growth. With efficient governance, expanding connectivity, and sectoral strengths in minerals, energy, agro-processing, and apparel, Chhattisgarh is well positioned for sustained and diversified economic development.




