Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyaan
Introduction
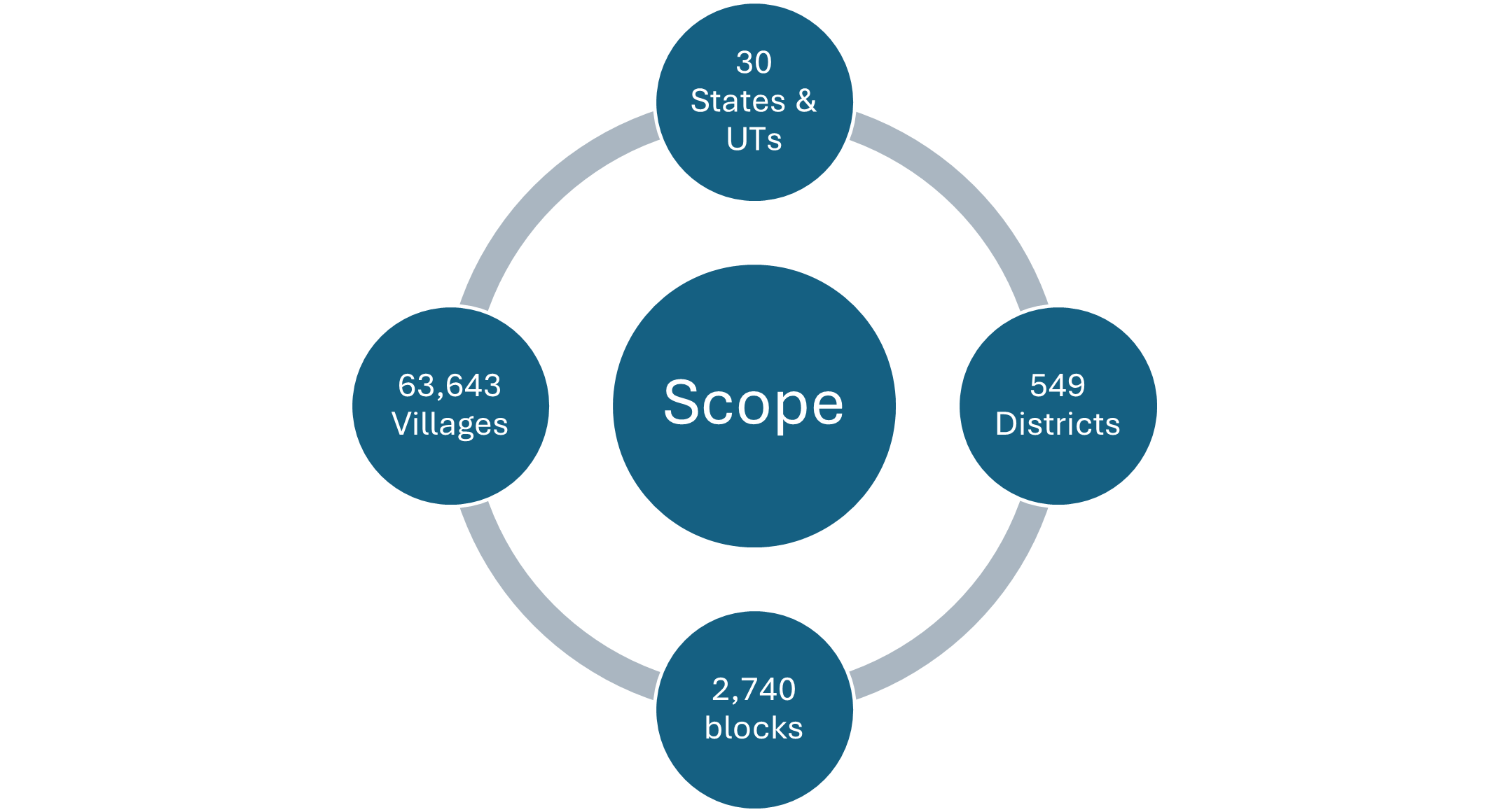
As per the 2011 Census, the Scheduled Tribal (ST) population in India exceeds 10.45 crore, constitutes over 8.6% of the total population and 11.3% of the total rural population. While there has been improvement in socio-economic development, tribal groups remain in remote and hard-to-reach places and face significant challenges in education, healthcare infrastructure and livelihoods.
In the post-Independence period, government programmes such as Tribal-Sub-Plan (TSP) and Development Action Plan for Scheduled Tribes (DAPST) aimed to rectify these problems, but their impact remains inconsistent. The government aims for complete development of tribal areas by bridging gaps through the Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyaan (PMJUGA). The mission aims to drive inclusive, sustainable growth and empower tribal communities to overcome the basic infrastructure and socio-economic challenges by merging a few government schemes.
Objectives
The main goals of the initiative are:
Goal – 1: Developing enabling infrastructure
In tribal areas, this initiative focuses to refine basic infrastructure, including construction of pucca houses under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) for eligible ST beneficiaries. Moreover, it aims to provide access to tapped water under the Jal Jeevan Mission and improve the quality of power supply under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS). Along with these efforts, road connectivity under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), mobile and internet access under BharatNet, and infrastructure for health, education and nutrition under the National Health Mission, Samagra Shiksha and Poshan programmes, respectively, are being improved. Eligible ST households will also have access to gas connection provided through the Ujjwala Yojana and health coverage through the Ayushman Bharat Card (PMJAY).
Goal – 2: Promotion of economic empowerment
The programme aims to elevate economic self-reliance by improving skill development and entrepreneurship among ST youth through programmes such as the Skill India Mission and Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS). It also supports livelihoods through Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMC), promotes Tourist Home Stays, and strengthens agriculture, animal husbandry and fisheries for FRA Patta holders.
Goal – 3: Universalisation of access to education
To optimise access to education, the Abhiyaan targets achieving high Gross Enrolment Ratios (GER) for ST students and supports infrastructure improvements, financial aid and digital learning. It also provides tribal hostels to facilitate education, especially in remote areas, ensuring tribal children can access quality education from school to higher education.
Goal – 4: Healthy life and dignified ageing
This objective focuses on boosting healthcare for ST communities by improving Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) and immunisation coverage. It includes the deployment of Mobile Medical Units (MMUs) in remote areas and the establishment of Centres of Competency for Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) management.
Timeline for implementation
The initiative will be conducted over seven phases from 2024 to 2029, with each phase concentrating on specific activities, monitoring and scaling up interventions. Below is the proposed timeline:

Source: Department of Tribal and Scheduled Caste
Phase 1: Planning & Awareness (2024-2025)
- Stakeholder engagement: Identifying local stakeholders, including village panchayats, NGOs and educational institutions.
- Awareness campaigns: A combination of traditional outreach and digital media (such as social media, radio and workshops) to inform communities about Abhiyaan’s benefits, especially focusing on sustainable agriculture, water management and renewable energy.
- Village baseline surveys: Conducting participatory rural appraisals and detailed surveys to understand local needs and create Detailed Project Reports (DPRs).
- Digital campaigns: Using platforms such as WhatsApp, YouTube and local radio to share success stories and model interventions.
Phase 2: Model Implementation (2024-2026)
- Demonstrative projects: Implementing pilot interventions in selected villages as model villages, focusing on social security benefits, including providing Ayushman Bharat cards, medical mobile units and access to electricity and water connections.
- Local participation: Engaging local communities in on-site demonstrations of innovative agricultural practices and renewable energy solutions.
- Incentives and competitions: Organising competitions and reward schemes for communities adopting new practices, such as water conservation or organic farming.
- Livelihood support: Establishing Tribal Multipurpose Marketing Centres (TMMC) to improve income opportunities for artisans and producers.
Phase 3: Financial Mobilisation (2024-2025)
- Government funding: Securing funding from central and state budgets earmarked for rural development, agriculture and energy.
- CSR and private partnerships: Encouraging Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) investments for rural development.
- Local resource utilisation: Promoting the use of local materials, labour, and knowledge to ensure sustainable resource management.
Phase 4: Convergence with Other Government Schemes (2024-2029)
- Leveraging existing programmes: Aligning the Abhiyaan with ongoing governmental initiatives, such as PMAY, MGNREGA, PMKSY and Ayushman Bharat.
- Integrating with rural employment schemes: Using MGNREGA for labour-intensive infrastructure projects, such as road construction and watershed management.
- Focusing on health and education: Enhancing tribal access to healthcare and education through collaboration with Ayushman Bharat, Samagra Shiksha and other schemes.
Phase 5: Scaling & Monitoring (2027-2029)
- Scale-up: Expanding successful model village interventions to cover a broader range of tribal villages.
- Monitoring systems: Establishing robust systems for monitoring progress, including local committees, GIS mapping and mobile apps to track outcomes.
- Data integration: Using technology to integrate performance data and ensure transparent tracking of physical and financial progress.
Phase 6: Monitoring & Evaluation (2024-2029)
- Key performance indicators (KPIs): Defining and tracking KPIs such as health outcomes, school enrolment rates, employment generation and agricultural yields.
- Third-party audits: Conducting regular third-party evaluations to ensure transparency and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
- Impact assessment: Periodically assessing the long-term impact of the Abhiyaan to identify areas for improvement.
Phase 7: Sustainability & Exit Strategy (2028-2029)
- Community ownership: Gradually transferring the management of local projects to Community-Based Organisations (CBOs) to ensure sustainability.
- Capacity building: Continuing to build local capacities so that communities can independently manage programmes.
- Institutionalisation: Integrating successful interventions into existing government programmes to ensure long-term sustainability and continued benefits for tribal communities.
Key activities
The key activities are outlined below across four levels:
Central level activities
- Policy development: Developing national policies and guidelines that ensure uniformity and clarity to implement the programmes across all states and regions.
- Funding allocation: Allocating and managing financial resources for the mission, assuring sustainable and timely disbursement to the appropriate states and districts.
- Inter-Ministerial coordination: Coordinating across different ministries for an integrated schedule in executing the mission. Tribal Affairs, Rural Development, Health, Education and other ministries will work in synergy.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Overseeing the overall progress of the programme, evaluating its impact and ensuring that outcomes match with the government’s set objectives. Financial and physical progress will be tracked by a central authority.
State level activities
- Customisation of programmes: Adapting central guidelines to meet state-specific contexts and requirements, ensuring that interventions are relevant to local needs.
- Resource distribution: Managing the distribution of financial and material resources to districts and blocks, ensuring equitable access to the programme’s benefits.
- Training and capacity building: Conducting training programmes for local officials and key stakeholders, building capacity for effective programme implementation.
- Coordination and implementation: Coordinating the activities of various state departments, ensuring that implementation aligns with central guidelines. Regular monitoring and review of progress will also be conducted at the state level.
District level activities
- Data check and monitoring: Monitoring the progress of programme implementation at the district level and reporting to state and central authorities. This includes tracking key performance indicators and ensuring that targets are met.
- Stakeholder engagement: Engaging with local communities, NGOs and other relevant stakeholders for the effective rollout of the programme, ensuring their active participation.
- Field-level implementation review: Reviewing field-level activities to ensure that on-ground implementation aligns with the objectives of the mission. Regular reporting of progress will be required.
Block level activities
- Village Camps, IEC, Saturation Drives: Conducting Information, Education and Communication (IEC) campaigns at the village level, using saturation drives to spread awareness about the programme's benefits and services.
- Ground-level execution: Ensuring the effective execution of schemes at the grassroots level, including infrastructure development, health services, education and livelihood activities.
- Beneficiary identification and support: Identifying eligible beneficiaries in the target communities and ensuring they receive the full benefits of the programme, such as Ayushman Bharat cards, housing and education support.
- Village planning and community mobilisation: Involving local Community-Based Organisations (CBOs), conducting village-level planning sessions, and mobilising community support to drive ownership and ensure successful implementation of the programme.
Interventions
The initiative includes a wide array of interventions, spread across 17 ministries, with a focus on improving infrastructure, providing social services and enhancing livelihoods for tribal communities. These interventions are designed to address the specific needs of tribal areas and are aimed at ensuring holistic development, sustainability and empowerment.
- Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD)
Pucca Houses (PMAY-Gramin): Constructing 20 lakh houses for tribal households under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G).
Road Connectivity (PMGSY): Constructing 25,000 km of roads to connect remote tribal villages.
- Ministry of Jal Shakti
Water Supply - Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM): Providing functional household tap connections (FHTC) to every household and community water taps for hamlets with ≤ 20 households.
- Ministry of Power
House Electrification (RDSS): Electrifying every unelectrified household and unconnected public institutions under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS).
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy
Solar Power Scheme (Off-grid Solar): Providing off-grid solar power systems for unelectrified households and public institutions not connected to the electricity grid.
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
Mobile Medical Units (National Health Mission): Setting up around 1,000 mobile medical units to provide healthcare in remote areas where health facilities are beyond 5 km in hilly areas and 10 km in plain areas.
Ayushman Bharat (PMJAY): Providing coverage for every eligible household under the Ayushman Bharat health insurance scheme.
- Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
LPG Connections (PM Ujjwala Yojana): Providing 25 lakh LPG connections to eligible tribal households.
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
Anganwadi Centres (Poshan Abhiyan): Establishing 8,000 new Anganwadi Centres, including the upgradation of 6,000 existing centres to “Saksham” Anganwadis.
- Ministry of Education
Hostel Construction (Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan): Constructing 1,000 hostels to support education for tribal children.
- Ministry of AYUSH
Poshan Vatikas: Establishing 700 Poshan Vatikas (nutrition gardens) under the National AYUSH Mission.
- Department of Telecom
Universal Service Obligation Fund/BharatNet: Providing broadband connectivity to 5,000 tribal villages under the BharatNet initiative.
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Skill India Mission: Establishing 1,000 Vocational Development and Training Centres (VDVKs) to provide skill development opportunities for tribal communities.
- Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology
Digital Initiatives: Implementing digital initiatives to enhance access to information and services for tribal communities, with an annual fund allocation of ₹50 crore.
- Ministry of Agriculture & Farmer Welfare
Sustainable Agriculture Support: Promoting sustainable agriculture practices for Forest Rights Act (FRA) patta holders, benefitting approximately 2 lakh households.
- Department of Fisheries
Fish Culture Support (PMMSY): Promoting aquaculture for 10,000 community-level and 1,00,000 individual beneficiaries under the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying
Livestock Rearing Support (National Livestock Mission): Providing support to 8,500 individual/group beneficiaries for livestock rearing under the National Livestock Mission (NLM).
- Ministry of Panchayati Raj
Capacity Building (Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan): Providing training for Gram Sabhas and officers on Forest Rights Act (FRA) and other key local governance issues.
- Ministry of Tourism
Tribal Homestays (Swadesh Darshan): Developing 1,000 tribal homestays with financial support of up to Rs. 5 lakh (US$ 5,925) for new construction, Rs. 3 lakh (US$ 3,555) for renovation and Rs. 5 lakh (US$ 5,925) for village community requirements.
- Ministry of Tribal Affairs
PMAAGY - Multi-sectoral Interventions: Expanding the PMAAGY scheme to include 100 Tribal Multi-purpose Marketing Centres, improving the infrastructure of Ashram Schools, hostels, government/state tribal residential schools, and setting up Centres of Competence for Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) management.
FRA & CFR Management: Supporting the establishment of FRA Cells and the implementation of Community Forest Rights (CFR) Management Plans, with a focus on ensuring better management and protection of tribal forest rights.
Budget Allocation
The Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM-JUGA) has been approved with a total allocation of Rs. 79,156 crore (US$ 9.27 billion), comprising Rs. 56,333 crore (US$ 6.60 billion) from the Centre and Rs. 22,823 crore (US$ 2.67 billion) from the States.
The Ministry of Tribal Affairs received a significant increase in its budget allocation in the Union Budget 2025-26, with Rs. 14,925.81 crore (US$ 1.75 billion) allocated, a 45.79% increase from the previous year.
The Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DA-JGUA), originally named the PM Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM-JUGA), received Rs. 2,000 crore (US$ 234 million), a fourfold increase from Rs. 500 crore (US$ 59 million). This funding aims to enhance infrastructure, education, and livelihoods in tribal regions.
Conclusion
The Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PMJUGA) is determined to uplift tribal communities through sustainable development, with an importance on improving infrastructure, livelihoods and access to essential services. By cultivating skill development and self-reliance, the initiative looks forward to enhance education, healthcare and the overall quality of life, helping to bridge the development divide and amplify the voices of tribal populations across India.




