SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (18)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
BharatNet Unplugged: Transforming Rural Connectivity in India

- Aug 21, 2025, 15:10
- Infrastructure
- IBEF
Digitalisation is playing an important role in the development and evolution of communication, education, healthcare and the economy in India. Most of India’s population lives in rural areas, with limited or no access to high-speed internet. In today’s digital era, internet connectivity has become a primary need. To address this digital gap, in October 2011, the Indian government launched the National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) programme. In July 2015, the scheme was revised and renamed as the BharatNet project. It is one of the world's largest rural broadband connectivity initiatives. The project mainly aims at establishing digital connectivity in all of India's villages and gram panchayats by providing affordable, high-speed broadband connectivity.
Phases of BharatNet
BharatNet is a major project initiated by the Indian government to transform rural connectivity in the country. To ensure the successful implementation of this big mission, its execution has been divided into three phases:

Transforming rural connectivity in India
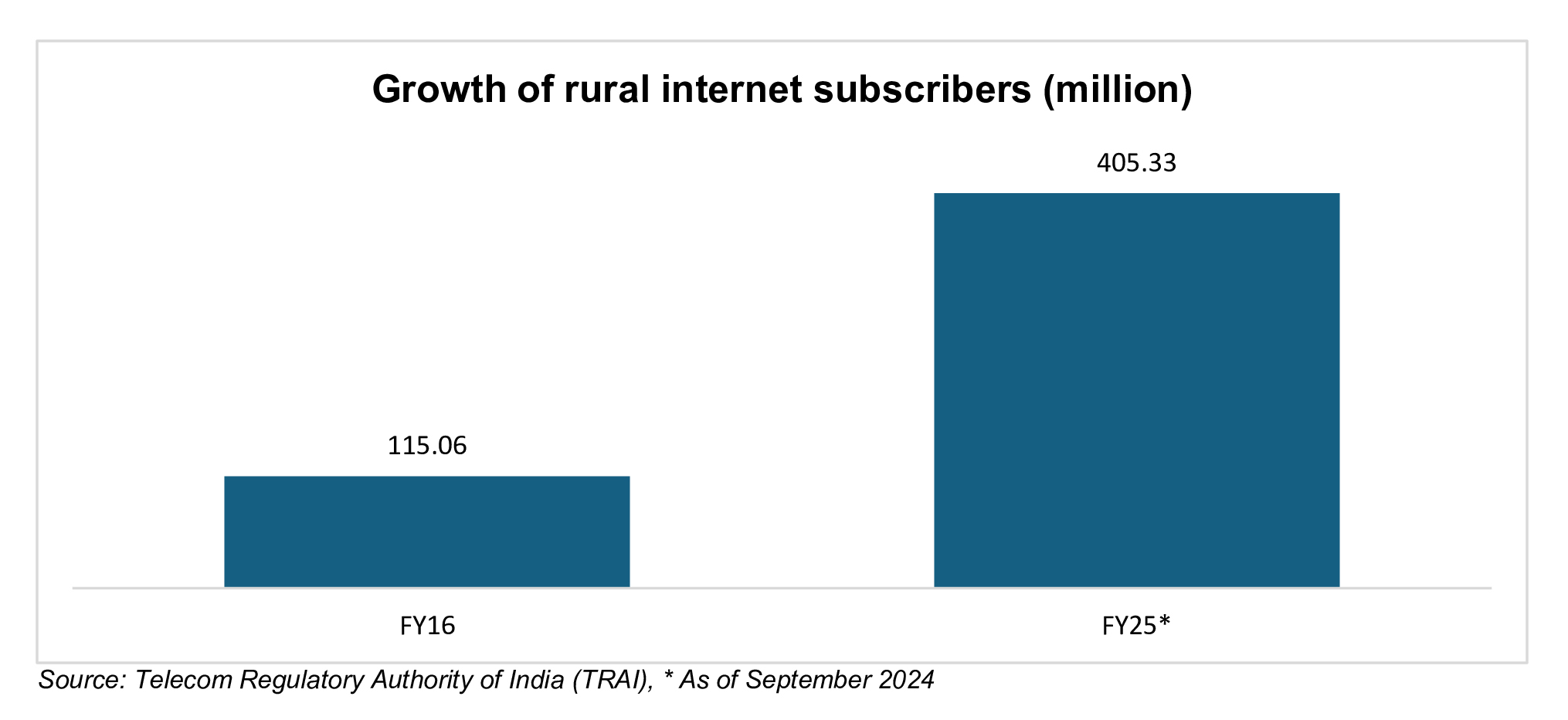
As of December 2024, Phase I and Phase II had collectively made significant progress by connecting over 2.14 lakh gram panchayats through 6,92,299 km of optical fibre cables (OFCs), 11.74 lakh FTTH connections and 1.04 lakh Wi-Fi hotspots. The median mobile broadband speed in India has increased to 95.67 Mbps with the cost of data reduced drastically to Rs. 9.08 (US$ 0.11) per GB. The number of internet subscribers in rural areas has increased significantly due to BharatNet. From 115.06 million in FY16, it has risen to 405.33 million by September 2024 in FY25.
Implementation models
- CPSU model: The CPSU model consists of central government agencies like BSNL, RailTel and Power Grid, which are responsible for handling and implementing the planning, construction and maintenance of the project. These established public sector entities bring expertise and resources for the execution of the project. The CPSUs have experience in handling large-scale infrastructure projects and can leverage their existing network and assets.
- State-led model: In this model, the states are responsible for implementing the BharatNet project. A fixed amount is provided by the central government for effective execution. This approach enhances the efficiency, effectiveness and sustainability of the project by leveraging local expertise, resources and governance structures. It promotes faster execution and better integration of state policies leading to an impactful outcome for digital connectivity and development.
- Private sector participation: In this model, the government allowed private companies to join the project in Phase II to bring in fresh ideas and enhance efficiency. These companies were picked through fair competition and brought their own resources and skills. This collaboration has enabled faster execution and improvement in service quality and customer experience.
BharatNet’s assistance to rural connectivity
Technologies used
To enhance rural connectivity even in remote and hilly regions, BharatNet employs a mix of technologies:
Optical fibre cables: This is the primary technology used for establishing high-speed internet connectivity in rural areas. OFCs are super thin, long glass or plastic strands that can carry significant amounts of information. They use light instead of electricity, enabling fast, smooth, clear and disturbance-free communication over long distances.
Satellite links: Satellite links are like invisible bridges in the sky that help send information from one place to another using satellites. They are important for connecting places that are far apart or difficult to reach, like remote and hilly regions, where laying OFCs is difficult.
Wireless technologies: Wireless technologies use radio waves or other types of signals to send and receive information without using physical wires, making it easier and cheaper to establish last-mile connectivity in rural areas. These help cover large areas, making sure more people can get internet access.
Impact and benefits of BharatNet
- Digital empowerment: BharatNet can help over 60 crore people in rural India to become part of the digital world. With internet access, villagers can apply for government schemes, get certificates and access essential services from their smartphones or nearby service centres.
- Economic growth: Internet connectivity helps boost local economies by enabling new activities. Farmers can use mobile apps to check weather updates and market prices. Small businesses can accept digital payments. People can even work remotely from their villages or run local BPO centres.
- Education and healthcare: Students in rural areas no longer have to depend only on schoolbooks; they can attend online classes, watch educational videos and prepare for exams. Clinics in villages can also offer better care using video consultations and digital health records.
- Governance and transparency: Digital tools help village officials work more efficiently. They can send real-time data to higher authorities, manage welfare programmes online and handle public complaints through portals. Systems like Aadhaar and DBT ensure benefits reach the right people without delays.
Opportunities for BharatNet
- Strengthening last-mile connectivity: It is important not just to connect the village office but to reach every home, school and clinic. Solutions like FTTH and strong Wi-Fi networks can make the internet usable for everyone, not just officials.
- Promoting digital literacy: People need to be trained on how to use online services. Digital literacy programmes, especially for women, students and farmers, can unlock the full potential of BharatNet and increase its adoption.
- Ensuring sustainability: Prolonged reliability on government funds needs to be replaced with sustainable revenue models. Encouraging local entrepreneurs, small ISPs and public-private partnerships can make the network sufficient over time.
- Policy support: The government increased the initial allocation of Rs. 20,000 crore (US$ 2.34 billion) for the BharatNet project in 2017 to Rs. 22,000 crore (US$ 2.57 billion) in the Union Budget for 2025-26. Along with financial support, the government should provide clear guidelines, fast-track approvals and other incentives. Streamlining policies and coordination between different departments can help speed up implementation and improve results.
Summing up
BharatNet can prove to be a game changer in India’s growth and development. It aims to close the digital gap by bringing high-speed internet to rural areas. This will give millions of people access to important services, education and new economic opportunities. BharatNet is funded through the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF), managed by the Ministry of Communications. This investment will build better digital services and strong infrastructure. It will also help India's telecom industry become more self-reliant. The project has made significant progress, connecting over 2.14 lakh village councils by 2024 using various technologies and a phased approach. However, challenges remain, such as low digital literacy and delays in implementation. By addressing these issues, BharatNet can boost growth and digital inclusion in rural India.
















