SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (35)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (18)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (57)
- Textiles (8)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
Preventive Healthcare in India

- Nov 10, 2023, 00:05
- Healthcare
- IBEF
Curative medicine has historically taken precedence over preventive treatment in India. However, as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic, preventive care has become increasingly crucial in India. A recent poll of more than 1,000 people revealed that at least 40% of respondents strongly preferred preventative health. NCDs have been the primary cause of mortality and suffering during the last three decades, accounting for 71% of global deaths. In 2019, India was responsible for 66% of all deaths. Furthermore, more than half of these deaths are caused by heart disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disorders, and diabetes. The economic burden of NCDs on India is anticipated to be over Rs. 511 lakh crore (US$ 6.2 trillion) by 2030. Overweight and obesity alone affect over 17% of our population, costing the country Rs. 2.8 lakh crore (US$ 35 billion) every year, or more than 1% of its GDP.
The preventive healthcare sector, which includes exercise, wellness, foods and supplements, early diagnoses, and health tracking, is estimated to reach US$ 197 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 22%. Healthcare start-ups in India have attracted investments totalling more than US$ 150 million. These start-ups are transforming healthcare delivery in categories such as nutrition, wellness, cancer, genomics, and others. In recent years, healthcare start-ups have revolutionised preventative care in areas such as nutrition, wellness, cancer, genetics, and much more. The necessity of the hour is to implement new technological developments to successfully supply high-quality healthcare to a billion people across India. Preventive care has undergone a revolution in terms of accuracy and speed due to technological disruption and New Age technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the IoT, especially in the wake of the pandemic. As part of its strategy to combat this epidemic, the Government has implemented several public health initiatives. The National Programme for the Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke (NPCDCS) raises awareness, establishes infrastructure (such as community health centres, NCD clinics, and cardiac care units), and conducts opportunistic screening at the primary health care level. There are also plans to reduce household consumption of solid fuels and tobacco smoking by 2025.
Healthcare in India
In the medical and healthcare fields, the terms "curative" and "preventive" refer to the two types of healthcare.
Curative Healthcare
Its primary goal is the treatment of disease or the acceleration of the recovery from an impairment, accident, or illness. The goal is to resolve any ailment and return the patient to their pre-illness state of health. It covers basic medical interventions, such as the use of antibiotics to treat strep throat and other bacterial diseases. Chemotherapy treatments can be used to treat a variety of cancers. Curative healthcare, which will account for 64% of total healthcare spending in India in 2021-22, is expanding at an annual rate of 15%.
Preventative Healthcare
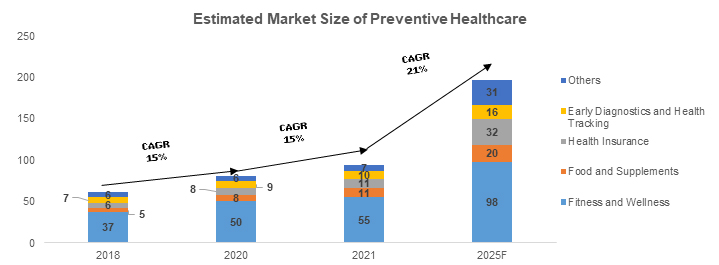
Source: Reedser Consulting, Chiratae Ventures and Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Note:F-Forecast
The basic goal of preventive healthcare is to prevent illness before it occurs. It is also called Prophylaxis. The philosophy underlying preventative healthcare is to protect, promote, and preserve one's health and well-being. It also tries to prevent sickness, disability, and mortality on an individual and community level. Preventive health involves the discovery and reduction of disease risk factors, the improvement of the course of an existing disease, and early disease detection through screening. Preventive healthcare is an important aspect in defining health since it comprises avoiding or postponing the start of a sickness, which is critical for a high quality of life.

1. Social Media Stack
Social media platforms are being used to democratise preventive healthcare by educating people and raising awareness about health issues. Startups, for example, use social media data to personalise wellness products.
2. Proprietary Data stack
Startups employ a variety of strategies to gather or acquire health data, including customer data, partner/purchase data, and firm acquisition. They construct data stacks that can be analysed using Artificial Intelligence (Al) or Machine Learning (ML) to make sound decisions.
3. Collaboration Stack
The implementation of ABDM will promote healthcare data interoperability, resulting in consumer-consent-based data availability for preventative health businesses. As a result, startups will be able to provide personalised solutions across nutrition, fitness, disease management, and insurance.
Framework
The foundational pillars for startups delivering preventive healthcare in India are the 3As-Awareness, Accessibility and Affordability.

Stakeholders
1. Startups
Numerous firms, including BeatO, Plum, Onsurity, HealthifyMe, GOQii, and others, are addressing consumer requirements for a range of preventive healthcare services. Startups are leveraging the cloud to deploy technologies such as machine learning, analytics, and IoT to monitor health, lower core costs, improve collaboration, enable data-driven decision-making, and shorten innovation cycles.
2. Diversified Corporates
Diversified corporations like Reliance, Tata, Flipkart, and others are concentrating on providing healthcare services to their clients. For instance, Reliance Retail recently purchased a majority share in Netmeds, and Tata Digital recently invested in Cult. fit, and Flipkart created Flipkart Health+ to provide access to authentic medications and healthcare supplies.
3. Healthcare Corporates
Large healthcare corporations are taking advantage of additional opportunities in the healthcare value chain, including Apollo, Dr. Lal Path Labs, SRL Diagnostics, and others. For example, Apollo promotes preventive healthcare check-ups.

Opportunities
1. New age technologies
New technologies like Metaverse, Web 3.0, etc., are being incorporated by startups. For instance, GOQii plans to launch the health metaverse and create a number of services that use gamification and blockchain tokens to promote preventive healthcare.
2. Personalised care delivery
For example, HealthifyMe uses Rio, a virtual assistant built on the Al platform, to offer its consumers customised advice on fitness, diet, and health depending on their lifestyle habits.
3. Telehealth applications
Examples include vertical health apps like Mojocare. Smiles.ai offers a digital-first care layer that includes daily monitors, general consultative conversations, treatment planning (if applicable), and information through their applications.
4. Remote Monitoring
For instance, Dozee has introduced Dozee Pro, a contactless vitals monitor for hospitals that transforms any bed into a step-down KU in less than two minutes and allows remote monitoring of patients outside of the KU, improving patient care and clinical outcomes.
5. AI/ML-powered diagnostics
For example, 5C Networks has developed a technology platform that leverages Al and ML to accelerate medical scan results while maintaining a high level of accuracy.
6. Hardware-first innovations
For instance, Redcliffe recently tested a commercial drone corridor for sample collection in an inventive effort to increase access to early testing, which could result in early discovery among patients.
Investment Landscape

Source: Reedser Consulting, Chiratae Ventures and Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Government Initiatives
1. Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
The goal of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) is to build a national digital health ecosystem that supports universal health coverage in an effective, affordable, timely, inclusive, and safe manner. To achieve this, ABDM will provide a variety of data, information, and infrastructure services while appropriately utilising open, interoperable, standards-based digital systems. This ecosystem will also ensure the security, confidentiality, and privacy of personal health information.
2. National Health Mission (NHM)
The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and the National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) are two sub-missions of the National Health Mission (NHM). The primary components of NHM are Health System Strengthening, Reproductive-Maternal-Neonatal-Child and Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A), and Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases (NCD).
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke (NPCDCS)
The National Programme for the Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) was established in 2010 to prevent and control major non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Under the National Health Mission (NHM) programme focuses on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion and awareness generation for cancer prevention, early diagnosis, management, and referral to an appropriate level of healthcare facility for the treatment of Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs), including cancer. As of December 2022, there are 707 District NCD Clinics, 268 District Day Care Centres, and 5541 Community Health Centre NCD Clinics operating under the NPCDCS. - National Mental Health Programme (NMHP)
The National Mental Health Programme (NMHP), established by the Indian government in 1982, has the following goals:- To guarantee that everyone has access to a minimal level of mental healthcare in the near future, with a focus on the most disadvantaged and underprivileged segments of society.
- To promote the use of information about mental health in general healthcare and social development.
- To encourage community involvement in the creation of mental health services and to catalyse community-wide initiatives for self-help.
- National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCBVI)
The National Programme for Blindness Control was established with the purpose of reducing the prevalence of blindness from 1.4% to 0.3%. Initially, it was a completely government-sponsored scheme. According to the 12th Five Year Plan (FYP), it is 90:10 in hilly states and all NE States, and 60:40 in all other states and UTs. In 2017, the National Programme for Control of Blindness (NPCB) was renamed as the National Programme for Control of Blindness & Visual Impairment (NPCBVI). - National Programme for Healthcare of Elderly(NPHCE)
The initiative is state-oriented, with the primary goal of providing dedicated healthcare facilities to elderly persons (>60 years of age) at various levels of primary, secondary, and tertiary healthcare. - National Programme for The Prevention & Control of Deafness (NPPCD)
- To stop avoidable hearing loss brought on by illness or accident.
- Early detection, diagnosis, and care for ear conditions that cause hearing loss and deafness.
- To provide medical rehabilitation for deaf people of all ages.
- To make the inter-sectoral connections stronger so that the rehabilitation programmes for deaf people can continue.
- To build institutional capacity for ear care services by supporting the necessary tools and supplies and hiring staff.
- National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP)
During the 11th Five-Year Plan, the Government of India started the National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP) with the goal of:- To raise awareness about the detrimental effects of tobacco consumption.
- To decrease the manufacturing and distribution of tobacco goods.
- To ensure the "The Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act, 2003" (COTPA)" regulations are effectively implemented.
- Assisting those who want to quit smoking.
- To assist in implementing the tobacco preventive and control measures recommended by the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
- National Oral Health Programme(NOHP)
- To enhance the factors that influence oral health.
- To lessen oral disease-related morbidity.
- To incorporate preventive and promotion services for oral health into the system of general healthcare.
- To promote the Public Private Partnerships (PPP) model as a means of improving oral health.
- National Programme for Palliative Care (NPPC)
- Increase the ability of government health programmes like the National Programme for the Prevention and Control of Cancer, Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Stroke, the National Programme for the Health Care of the Elderly, the National AIDS Control Programme, and National Rural Health Mission to deliver palliative care services.
- Improve the legal and regulatory framework and assist its execution to ensure that opioids are accessible and readily available for use in medicine and research while preserving safeguards against diversion and misuse.
- Strengthen and include long-term care and palliative care ideas into the educational curricula (of medical, nursing, pharmacy, and social work courses) to promote attitude changes among healthcare workers.
- Encourage behavioural change in the community by raising public awareness and enhancing people's skills and knowledge in pain management and palliative care, which will result in locally owned projects that assist the healthcare system.
- Create national standards for palliative care services and continuously improve the National Program's design and execution to ensure progress towards the program's vision.
- National Programme for Prevention & Management of Burn Injuries (NPPMBI)
- To reduce burn injury incidence, death, morbidity, and disability.
- To increase awareness among the general public and vulnerable groups, particularly women, children, and those who work in industries or in hazardous occupations.
- To provide enough networks and infrastructure for interventions in behaviour change communication, burn management, and rehabilitation.
- To conduct research to evaluate the behavioural, social, and other factors that influence burn injuries in our nation in order to create, monitor, and ultimately evaluate effective need-based burn injury programmes.
- Other Non-Communicable Disease Control Programmes
- National Organ Tissue and Transplant Organization (NOTTO)
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Fluorosis (NPPCF)
- National Iodine Deficiency Disorders Control Programme
3. Fit India Movement
The Prime Minister of India started the FIT INDIA Movement on August 29th, 2019, with the goal of making exercise an intrinsic part of our daily lives. The Movement's objective is to promote behavioural changes and a more physically active lifestyle. Fit India proposes to undertake numerous projects and hold events to attain the following goals in order to achieve this mission:
- To promote fitness as simple, enjoyable, and cost-free.
- Through targeted efforts, raise awareness about fitness and other physical activities that enhance fitness.
- To encourage native sports.
- To provide fitness to every school, university, panchayat, and village, among other places.
- To establish a forum for Indian citizens to exchange knowledge, raise awareness, and promote the sharing of their own fitness-related experiences.
Road Ahead
India is undergoing a rapid health shift. The transition from curative to preventative care is also predicted to benefit the Indian consumer, with improved health outcomes and cheaper healthcare expenses.
Healthcare services are insufficient without preventive, promotional, and screening components. The advantages of prevention go beyond the management of chronic diseases and living longer lives. Preventive Health and Screening OPDs are critical in hospitals for mainstreaming health promotion and preventive healthcare. Investment in preventative healthcare minimises individual suffering, improves sickness outcomes, and significantly reduces the country's fiscal burden.
















