SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (18)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
Smart cities and Academia towards Action & Research (SAAR)

- Mar 30, 2022, 13:45
- Infrastructure
- IBEF
Introduction
India is among the largest economies in the world, with an urban population representing about 35% of the country’s total population (approximately 474 million in 2020). Being one of the top countries with the most populated cities in the world, India has taken several initiatives to develop and urbanise the country. As per a United Nations report, India will add around 416 million more people to its urban population by 2050. The country’s smart city and urbanisation mission is aimed at improving the quality of life of its population.
Smart Cities Mission
Launched in 2015, the objective of the Smart Cities Mission is to promote cities providing core infrastructure, clean and sustainable environment and decent quality of life to citizens by applying smart solutions. The mission of this centrally sponsored scheme is to drive economic growth and improve quality of life by focusing on the social, economic, physical and institutional pillars of cities.
Initially, 100 cities have been selected to be developed as smart cities. These cities are from 32 states and union territories of India, and the development is planned through a two-stage competition. The central government plans to provide financial support of about Rs. 100 crore (approximately US$ 13 million) to each city on yearly basis. The total amount planned under this mission is Rs. 205,018 crore (approximately US$ 27 billion) for the development of 5,151 projects in the 100 cities selected. In this mission, private sector participation was emphasised through Public Private Partnerships (PPP).

What is the SAAR program?
As part of the Azadi Ka Amrut Mahotsav (AKAM) celebrations, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) launched the SAAR programme under the Smart Cities Mission. It is a joint initiative of MoHUA, National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and some of the leading academic institutions in India.
The programme includes 15 premier planning institutions and 47 smart cities that will participate in 75 case studies. The institutes will work with the smart cities to document landmark projects undertaken as part of the Smart Cities Mission. This will help understand the practices and methods undertaken in the mission and help adopt the best practice for further projects.
Why was SAAR launched?
This programme was launched to capture learnings from the best practices undertaken by the urban planning and development of smart cities. The SAAR programme will also provide opportunities for engagement on urban development projects to students and enable an information flow between urban practitioners and academia. The main aim of this initiative is to expand the urban knowledge base and better understand the development plans that will be launched.
What is the process of SAAR?
Under the SAAR programme, initially, a compendium of 75 landmark urban projects in India under the Smart Cities Mission will be prepared. These projects are innovative, multi-sectoral and implemented across geographies. The 75 projects are spread across 47 smart cities. MoHUA and NIUA will facilitate the linkage between the institutions and the smart cities. A team of students and mentors from the institutions will visit the 47 smart cities selected and document the outcome of the projects and their impact on the lives of citizens.
The workflow of the compendium launch is as follows:
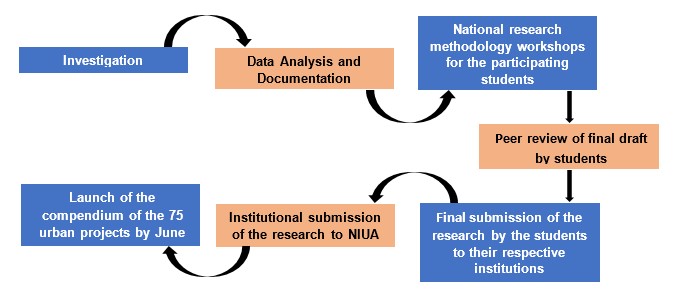
Smart cities that are part of the SAAR program
Several smart cities are selected for the SAAR programme as listed below:
|
Agra |
Ajmer |
Chandigarh |
Coimbatore |
Erode |
|
Kakinada |
Kochi |
Manguluru |
Shivamogga |
Thanjavur |
|
Thiruchirapalli |
Thiruvananthapuram |
Tumakuru |
Ahmedabad |
Dahod |
|
Nagpur |
Nashik |
Pune |
Surat |
Thane |
|
Vadodara |
Bhubaneswar |
New Town Kolkata |
Ranchi |
Vishakhapatnam |
|
Bhopal |
Gwalior |
Indore |
Raipur |
Sagar |
|
Ujjain |
Jabalpur |
Agartala |
Gangtok |
Namchi |
|
Dehradun |
Dharamshala |
Faridabad |
Jaipur |
Jammu |
|
Kanpur |
Saharanpur |
Shimla |
Srinagar |
Belgavi |
|
Bengaluru |
Chennai |
|
|
|
Institutes part of this programme:
The premier architecture and planning institutes selected for the SAAR event are as follows:
|
1 |
Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee |
|
2 |
Malaviya National Institute of Technology |
|
3 |
Jamia Millia Islamia, Delhi |
|
4 |
R V College of Architecture, Bangalore |
|
5 |
Anna University |
|
6 |
College of Engineering, Trivandrum |
|
7 |
Department of Architecture & Planning, Manipal University |
|
8 |
Centre for Environment Planning and Technology, Ahmedabad |
|
9 |
College of Engineering, Pune |
|
10 |
Kamla Raheja Vidyanidhi Institute for Architecture, Mumbai |
|
11 |
Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur |
|
12 |
Indian Institute of Science and Environment Technology, Shibpur |
|
13 |
School of Planning and Architecture, Vijayawada |
|
14 |
School of Planning and Architecture, Bhopal |
|
15 |
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology |
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA)
MoHUA is the apex authority that looks over the formulation and administration of laws and regulations concerning housing development and urban development of India. It also formulates policies; sponsors and supports programmes; and coordinates the activities of central ministries, state governments and other nodal agencies. Various divisions of the ministry look after different missions and development projects in the country such as urban renewal, public health, smart cities, transport, vigilance, works, budget, economics and finance.
The ministry has taken several initiatives such as Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework (CSCAF), India Cycle4Change Challenge, DataSmart Cities, Data Maturity Assessment Framework Cycle-2 (DMAF) and City Data Officer (CDO) for the betterment of urban areas and developing a knowledge base in cities.
National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA)
NIUA’s key focus is issues related to urbanisation. The institute works to bridge the gap between research and practices in urbanisation affairs and suggest methods to address the challenges better. NIUA is a data centre providing research used for urban planning and development.
The institute has five main centres:
- Climate Centre for Cities – policy, planning, project support, research and knowledge management, innovation, capacity building, partnerships
- Centre for Digital Governance – model policies and framework for digital governance, provide digital infrastructure, programme design and strategic advisory services, build shared digital technology
- Inclusive Cities Centre – spatial inclusion, social inclusion, economic inclusion, digital inclusion
- Centre for Municipal Finance and Governance – repository for municipal budgets, accounts, annual reports, assist various ministries and state governments on matters relating to municipal finance and governance
Centre for Urbanization and Economic Growth – diagnostic studies of emerging urban patterns and corridors, providing data on the linkage between economic growth and urbanisation, developing evidence-backed research

Conclusion
India is a fast-growing country with huge urbanisation potential. The government has been taking aggressive action for the development of a digital and smart India. The country has made a roadmap for smart city initiatives with investment plans of more than US$ 700 billion. The central and state governments are pushing for digital infrastructure and automation, and the country is moving towards sustainable business practices, which will help keep the pollution in check and protect the ecosystem. With rapid adoption of renewable energy, electric mobility and zero-emission targets, India can become one of the world’s leading urbanised countries.
















