SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (18)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
The Diaspora Effect: Driving Bilateral Ties and Remittances to India

The Indian story is not just limited to its borders, it is etched across continents, carrying the dreams and talent of millions of people. From techies in Silicon Valley to politicians in London parliament, from scientists in Nasa to healthcare workers in Doha, the Indian diaspora effect is advancing in every direction.
This global community is not only contributing to the economy but is now a powerful driver of foreign remittance to India, startup investments, cultural exchange and bilateral ties. They are transforming India’s economy and position on the world stage.
Remittances and beyond
As per Ministry of External Affairs, India had the world's largest diaspora, with over 35 million people of Indian origin living abroad (as of 2024). Prominent countries include:
- The United States: 5.41 million
- The United Arab Emirates: 3.57 million
- Malaysia: 2.91 million
- Canada: 2.88 million
- Saudi Arabia: 2.46 million
- Myanmar: 2 million
- The United Kingdom: 1.8 million
Spreading across 200 countries, they comprise Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs). They are a major economic asset, and their engagement extends across industries and helps develop stronger bilateral ties between India and their adopted countries.
Economic contributions
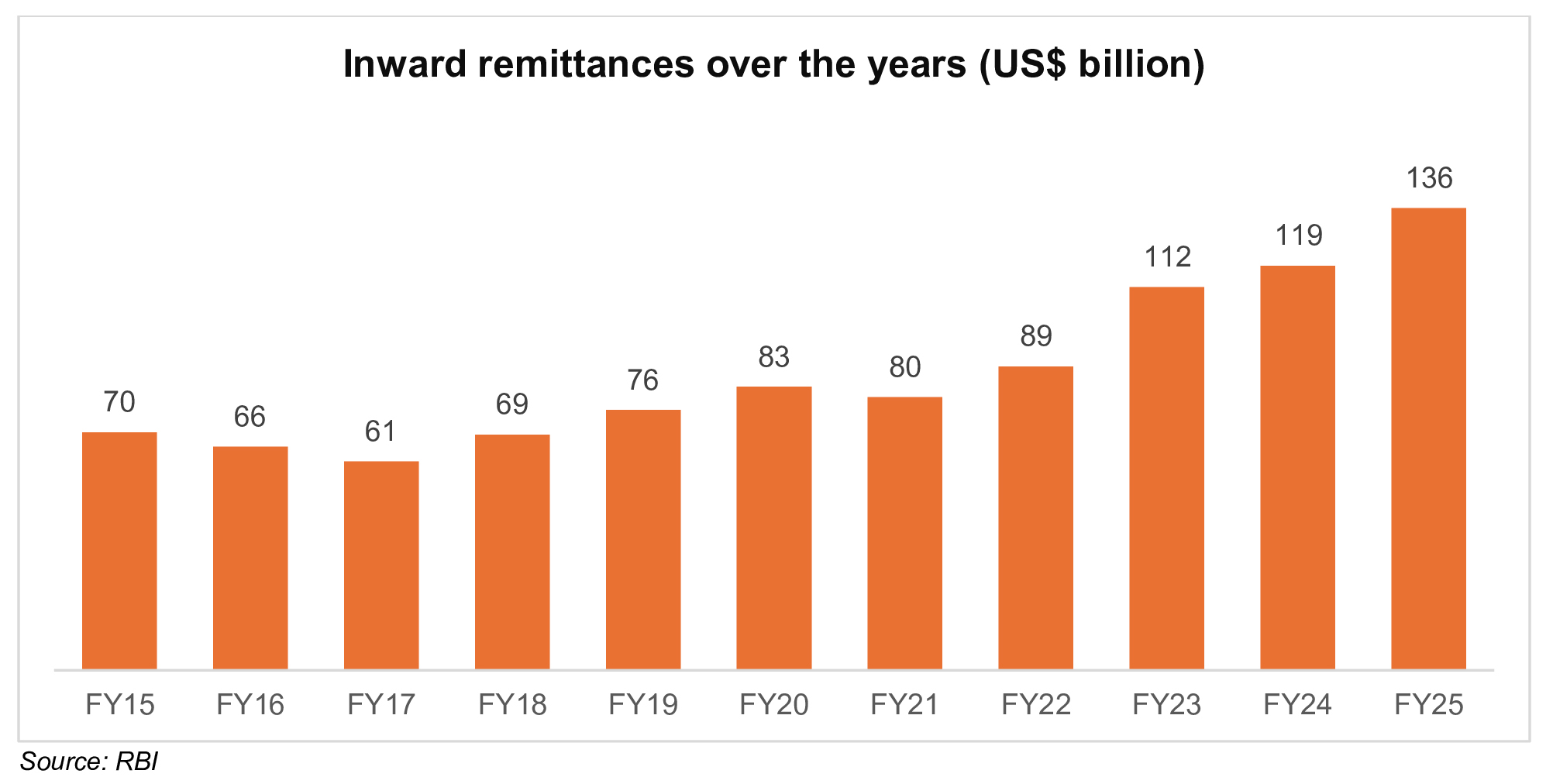
India has topped global remittances for over 25 years since the information technology boom in the 1990s and has consequently received over Rs. 8,56,700 crore (US$ 100 billion) for the fourth year in a row in FY25. In FY25, diaspora remittances hit a new record of Rs. 11,60,486 crore (US$ 136 billion) compared to Rs. 10,10,906 crore (US$ 119 billion) in FY24, a 14% increase YoY, according to Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
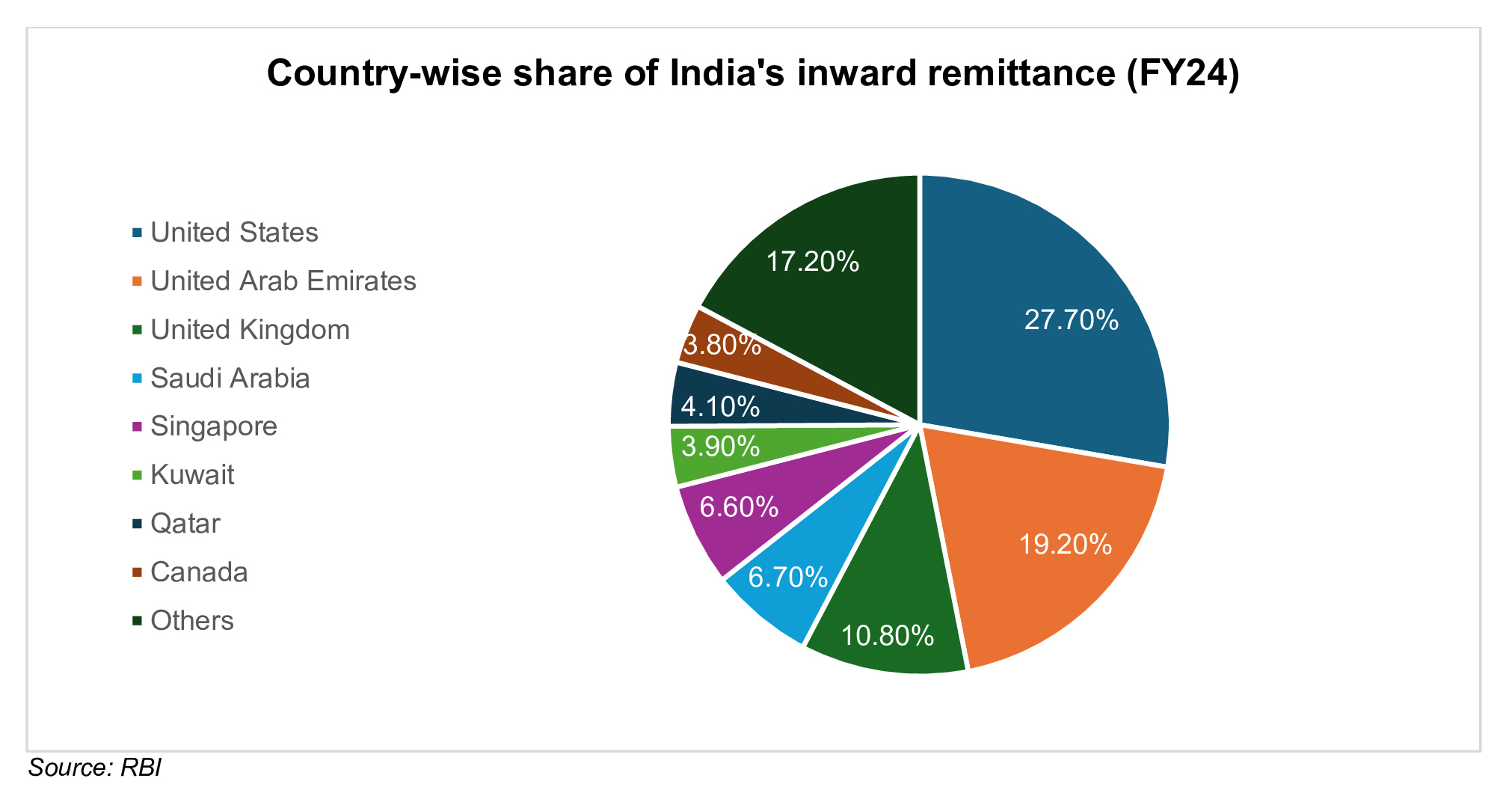
The data shows Indians are increasingly being concentrated in high-income economies, shifting the remittance trends towards technology-driven economies rather than gulf countries.
As per RBI, remittances contributed to over 10% of US$ 1 trillion of gross current account inflows in FY25. This substantial inflow helped cover India’s merchandise trade deficit, with remittances covering 47% of that gap. These inflows represent a reliable and supportive force for the Indian economy amidst volatile conditions, while simultaneously being a major source of income for the families.
Investment channels
The Indian diaspora is no longer limited to traditional banking and finance systems as various new investment opportunities are being introduced to increase the overall inflow of capital in the economy. Well known remittance channels that India offers include:
- Startups: Major Indian origin players and investment firms are actively investing in startups based in India. Mr. Sundar Pichai, Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Alphabet Inc. and its subsidiary Google, recently invested Rs. 309 crore (US$ 36 million) in a deep space startup based in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Real Estate: NRIs continue to invest heavily in Indian real estate. The growth has been steady over the years, rising from 10-12% in 2019 to 17-19% in 2024. Early projections for 2025 suggest it could reach an all-time high of 18-20% according to Mr. Akshat Shrivastava, CEO of Wisdom Hatch.
- Equities and Debt: Government initiatives such as Portfolio Investment scheme enables purchasing and selling of shares and debentures in the Indian market under repatriation and non-repatriation basis. In May 2025, Foreign Portfolio investors (FPI) infused Rs. 19,860 crore (US$ 2.31 billion), showing growing interest in the Indian economy.
- Philanthropy: NRIs have played a key role in India’s development through impactful philanthropy, supporting education, healthcare and grassroots initiatives. India Giving Day, a philanthropy event organised in the United States, raised Rs. 76 crore (US$ 8.86 million) in 2025 as compared to Rs. 47 crore (US$ 5.5 million) in 2024. Their contributions reflect a strong sense of responsibility and enduring connection to their roots.
Government approved platforms such as the India Development Foundation of Overseas Indians (IDF-OI) a government-established not-for-profit trust set up to enable overseas Indians to contribute to social and development initiatives in India and state-specific diaspora investment schemes, have made philanthropy and commercial investment easier and transparent.
Soft power diplomacy: Diaspora as economic ambassadors
The diaspora is one of the foundations of the Indian cultural diplomacy. The knowledge of Indian culture, food, music, dance, yoga, film and literature is spread by overseas Indians to the rest of the host societies, thus increasing India’s soft power. The diaspora groups organise annual festivals such as Diwali, Holi and numerous others being celebrated in the regions. The Indian film stars and writers living outside India also raise the profile of India.
Cultural institutions, especially Indian Council of Cultural Relations (ICCR) and State tourist boards, organise regular programmes in cooperation with members of the diaspora to represent India. The country’s diaspora has played a vital role in spreading yoga and enhancing the ‘Incredible India’ brand across the global markets. These moves create goodwill for India among other nations, which consequently results in smoother bilateral relations.
Whether one thinks of the former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Mr. Rishi Sunak, or Attorney and former Vice President of the United States, Ms. Kamala Harris, leaders of Indian origin demonstrate the growing global influence of India. They have also made the country’s diaspora the centre of the enhanced bilateral relationships. Their leadership highlights the accomplishments and integration of Indians in the foreign countries as they foster a more cordial work. This penetration extends to the corporate arena as well. So much so, that the leadership teams of some of the most powerful companies in the world are headed by CEOs of Indian descent, including:
- CEO of Alphabet, Mr. Sundar Pichai
- CEO of Microsoft, Mr. Satya Nadella
- Former CEO of PepsiCo, Ms. Indra Nooyi
- CEO of IBM, Mr. Arvind Krishna
- CEO of Adobe, Mr. Shantanu Narayen
- Former CEO of Twitter, Mr. Parag Agrawal
These global business leaders actively engage in India-global tech, trade and policy dialogues, often serving as informal ambassadors of Indian innovation, talent and values. Whether through corporate partnerships, diaspora investment or bilateral forums, they continue to shape the narrative of a globally connected and forward-looking India.
Strengthening India’s global economic ties
In general, there is a multiplier effect of diaspora on the development of India. According to RBI, 2-3% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is raised by remittances alone each year to meet the costs of imports and keep the rupee steady. The capital and trade relationships caused by the diaspora have enhanced India’s position in the global economy. Skilled returnees along with their foreign collaborators have seeded high-technology industries and research organisations.
The diaspora enhances the Indian image and visitation in terms of culture. The diaspora presence will remain a pillar of the country’s economic vibrancy, foreign outreach and artistic leadership as it blazes in that direction towards Viksit Bharat by 2047 and connects the nation to every quarter of the globe.
FAQs
What is the Diaspora Effect?
The Diaspora Effect refers to how over 35 million people of Indian origin living abroad advance India’s home economy, culture and bilateral ties through remittances, investments and soft power.
How large is India’s diaspora?
India’s diaspora exceeds 35 million across 200 countries, comprising NRIs and PIOs, with major communities in the United States (5.41 million) and the United Arab Emirates (3.57 million).
What was the annual remittances to India in FY25?
In FY25, annual remittance to India reached Rs. 11,60,486 crore (US$ 136 billion), up from Rs. 10,10,906 crore (US$ 119 billion) in FY24, marking a 14% increase.
What are the best investment / remittance channels that India offers?
Best remittance channels that India offers includes direct bank transfers, investments in startups, real estate, equities and debt under schemes such as the Portfolio Investment Scheme.
What are the various types of Indian government schemes to aid inward remittances?
Government‑approved platforms include the India Development Foundation of Overseas Indians (IDF‑OI) and state‑specific diaspora investment schemes to simplify philanthropy and commercial investment.
















