SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (68)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (24)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (33)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (17)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
Vegan Leather and the Future of Indian Leather Industry: A Sustainable Shift

- Aug 13, 2025, 11:20
- Manufacturing
- IBEF
The leather manufacturing industry plays an important role in the production of footwear, clothing, bags, belts, and other accessories. Traditional leather is derived from the hide or skin of animals, which is closely connected to the meat industry. However, manufacturing conventional leather requires toxic metals and chemicals as well as slaughtering of animals. These environmental concerns have led to the rise of sustainable, eco-friendly and cruelty-free leather production also known as vegan leather, faux leather or synthetic leather as well. Vegan leather is a plant-based material designed to impersonate the appearance and texture of traditional leather without using any animal-based by-products. The demand for vegan leather has gained prominence in the recent years as consumer preferences shift towards sustainable products.
Growth of vegan leather in India
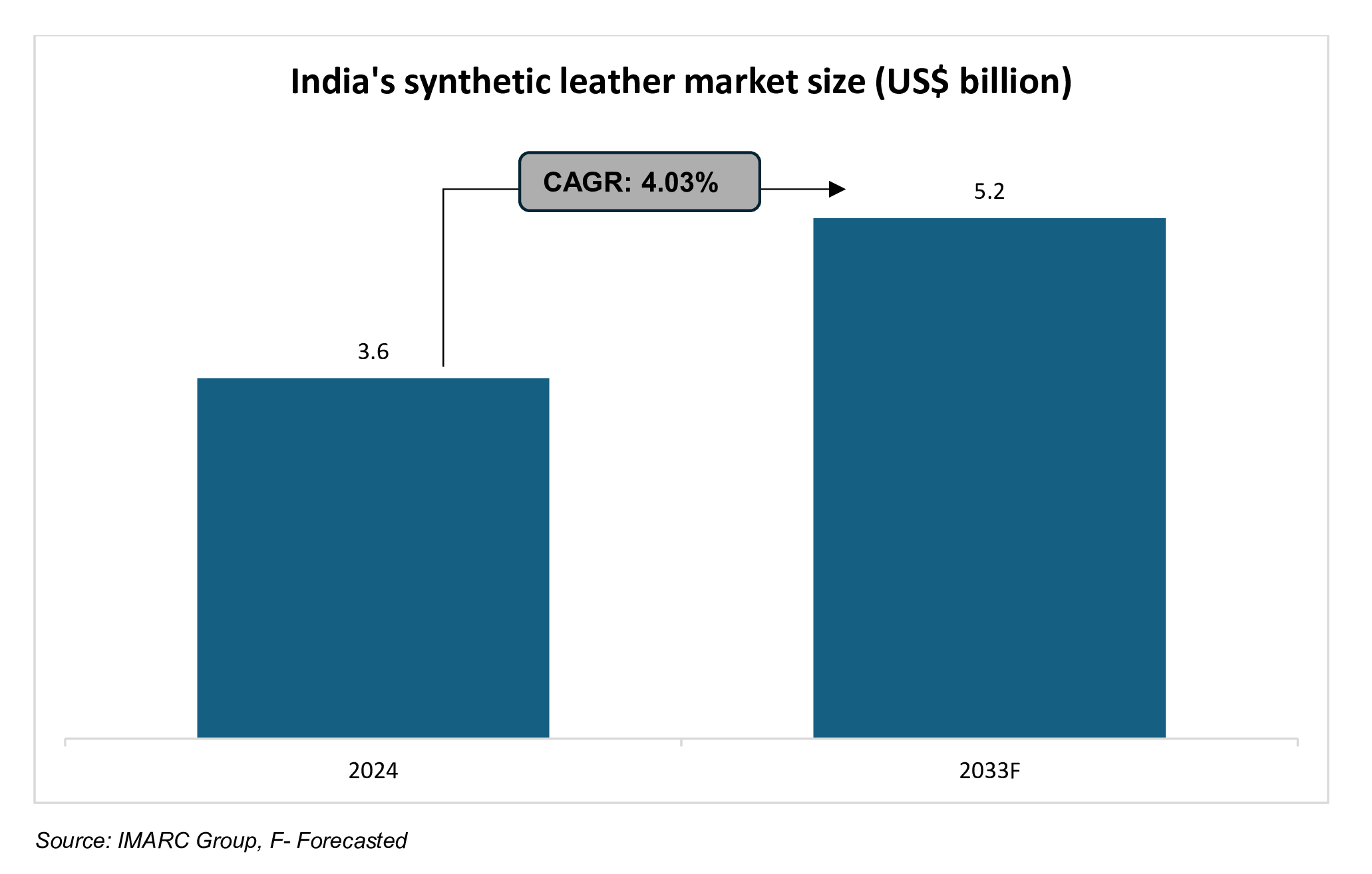
Leather has been recognised as the most vintage material and as a symbol of wealth, status and luxury due to its historical significance, high quality craftsmanship, and exclusivity. Whereas the rising consumer preferences for ethical, cruelty-free and sustainable products have led to a sustainable shift towards vegan leather products. Besides this the rise in the number of vegans and vegetarians has influenced the demand for cruelty-free products. India’s synthetic leather market stood at Rs. 31,396 crore (US$ 3.6 billion) in 2024. The market is expected to touch Rs. 45,349 crore (US$ 5.2 billion) by 2033, with CAGR of 4.03% during 2025-33.
Types of vegan leather in India
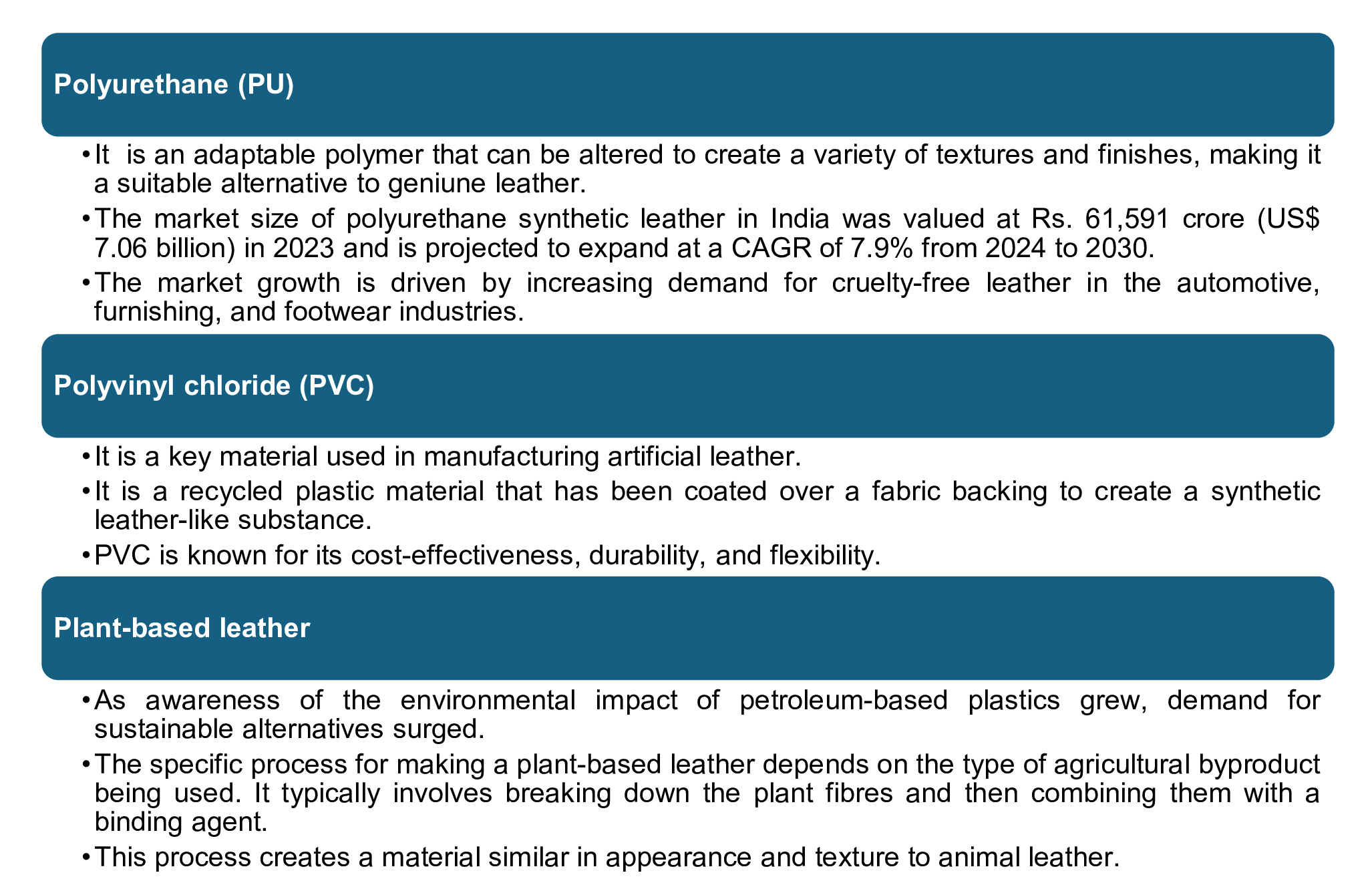
Raw materials recycled in plant-based vegan leather industry
Plant-based leather is a type of material made using a variety of plants and related materials, such as cork, bark, sugarcane bagasse, tea, cactus, coconut, banana leaf, mushroom, etc. Following are some of the agricultural products used to produce vegan leather:
- Apple leather: It mainly consists of apple waste generated from apple juice, i.e., the leftover pomace and peel of apple. It is also known as AppleSkin, a type of faux leather fabric. OEKO-TEX, recognised on international level for the testing of harmful substances in the textile and leather industry, has approved this plant-based leather as 100% cruelty-free.
- Leaf leather: As the name suggests, leaf leather is made using discarded plant leaves. This is a completely biodegradable and eco-friendly option that is highly sustainable and organic. It is used to create leather products such as bags, wallets, purses and other accessories.
- Piñatex leather: Piñatex is another plant-based leather made out of pineapple leaves. Leading fashion brands like Hugo Boss prefer the use of pineapple leaf-based leather as a biodegradable alternative to traditional leather.
- Mushroom leather: Mushroom leather is derived from Phellinusellipsoideus fungus or a mushroom. It is also known as MuSkin or mycelium leather as it is made from the root structure (mycelium) of fungi. It is very soft, water-resistant and biodegradable, making it a great alternative to traditional leather in apparel and accessories industries.
Indian start-ups and innovators in vegan leather
Indian startups and innovators are conducting extensive research to replace traditional leather. They are exploring various sustainable materials, such as upcycled floral waste, banana crop base, coconut water, sugarcane bagasse and many more plant-based sources, aiming to create eco-friendly alternatives to traditional leather.
- Phool: Phool is an Indian startup using floral waste to make vegan-friendly leather materials. It is manufactured from plant-based waste matter, that encourages the company to embrace circularity and sustainability. It is also called ‘Fleather’ as it is derived from flower waste. Leftover flowers collected from temples that would otherwise be discarded are recycled by this company. Flowers contain chitin, a natural polymer that gives the material strength and durability, making it a suitable alternative to animal leather.
- Banofi Leather: Banofi is an Indian company, that has introduced a groundbreaking plant-based leather made from banana crop waste. Generally, 10,000 litres of water is required to produce a single leather bag, Banofi has innovated a procedure that helps to reduce this water consumption, ensuring 100% reduction in toxic wastewater and cutting down carbon dioxide emissions by 90% compared to the traditional leather making process. This process has targeted the 120 million tons of banana waste generated on yearly basis. Additionally, the business supports one million banana farmers in India.
- Malai: Malai fabric is a bio-composite vegan leather made from bacterial cellulose grown using coconut water, a by-product of coconut harvesting. Natural fibres enhance its strength and flexibility. A small unit can process 4,000 litres daily, yielding 25 kg of bacterial cellulose. The fabric is flexible, durable, and naturally dyed without mordants, used for accessories and décor.
- PA Footwear P Ltd: PA Footwear P Ltd, in partnership with the National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology, has developed a leather alternative made primarily from sugarcane called as Vegan Virya. It comprises over 95% plant-based elements, prominently sugarcane bagasse, complemented by a 60% agro waste content. India is the second largest producer of sugarcane globally; so, this technology presents a significant opportunity to utilise sugarcane waste effectively.
The Indian leather industry is undergoing a sustainable shift towards vegan leather, encouraged by growing consumer demand for ethical and eco-friendly products. Innovations in plant-based materials, such as apple leather, leaf leather, and Piñatex, are leading the way. Many Indian startups have taken significant efforts to address the drawbacks of the traditional leather industry. With immense research and experiments, many vegan products are paving their way in the leather market. With growing awareness and technological advances, vegan leather is poised to transform the market, making it more sustainable and cruelty-free.
















