Assam
Assam has the single largest tea growing area in the world, constituting around one-seventh of the global tea production
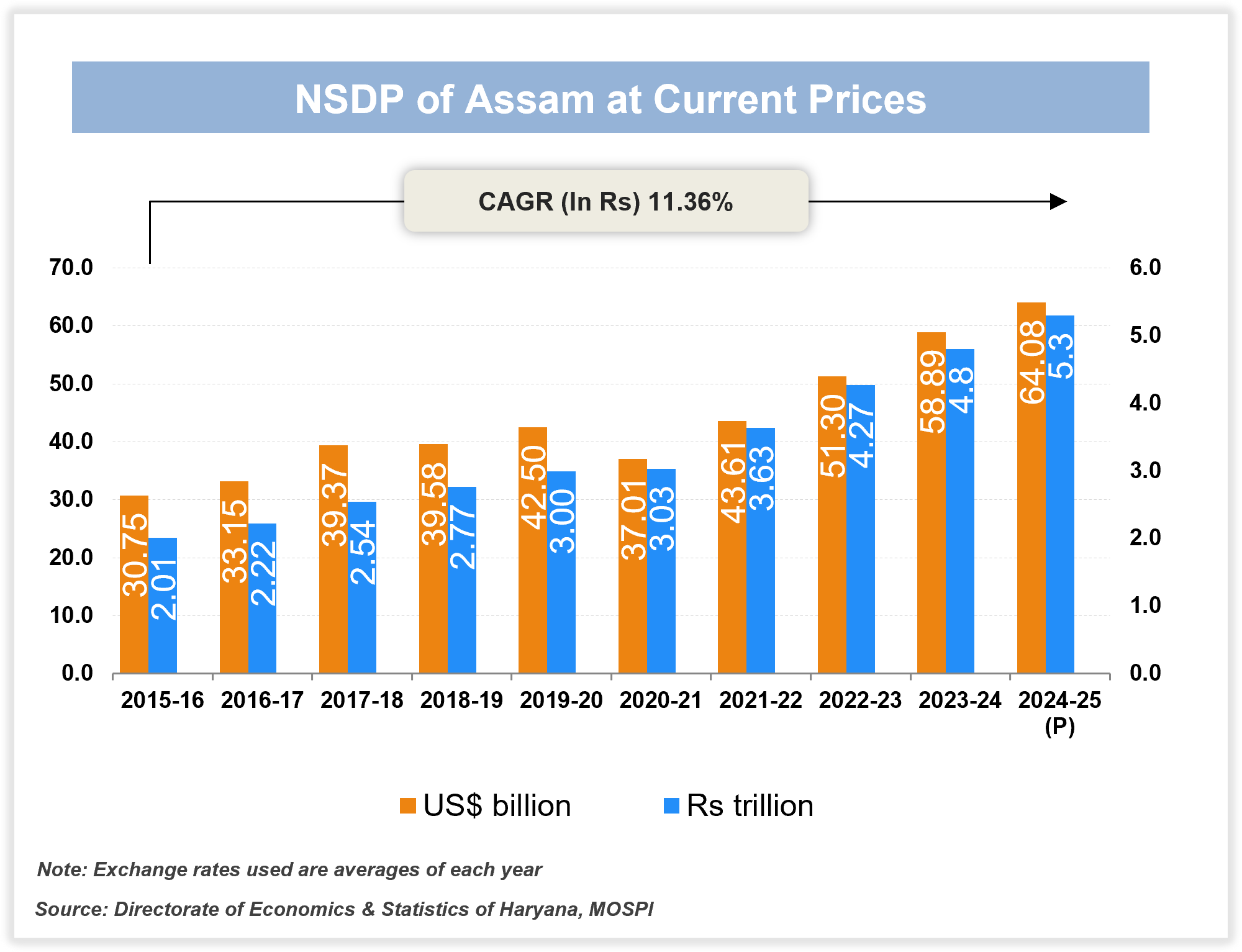
Assam is the largest economy in the northeast region. Owing to its relative proximity to the rest of the country and availability of quality infrastructure, the state offers a favourable environment for industry.
Assam has the largest tea-growing area in the world, constituting around one-seventh of the global tea production. In 2025 (January-September 2025), the state’s tea production stood at 497.33 million kgs.
It also has 20 industrial estates, three industrial growth centres, 11 Integrated Infrastructure Development Depots, 17 industrial areas, 12 growth centres, eight mini-industrial estates, one export promotion park and one food processing industrial park. Assam is also the most popular tourist destination among the northeast states.
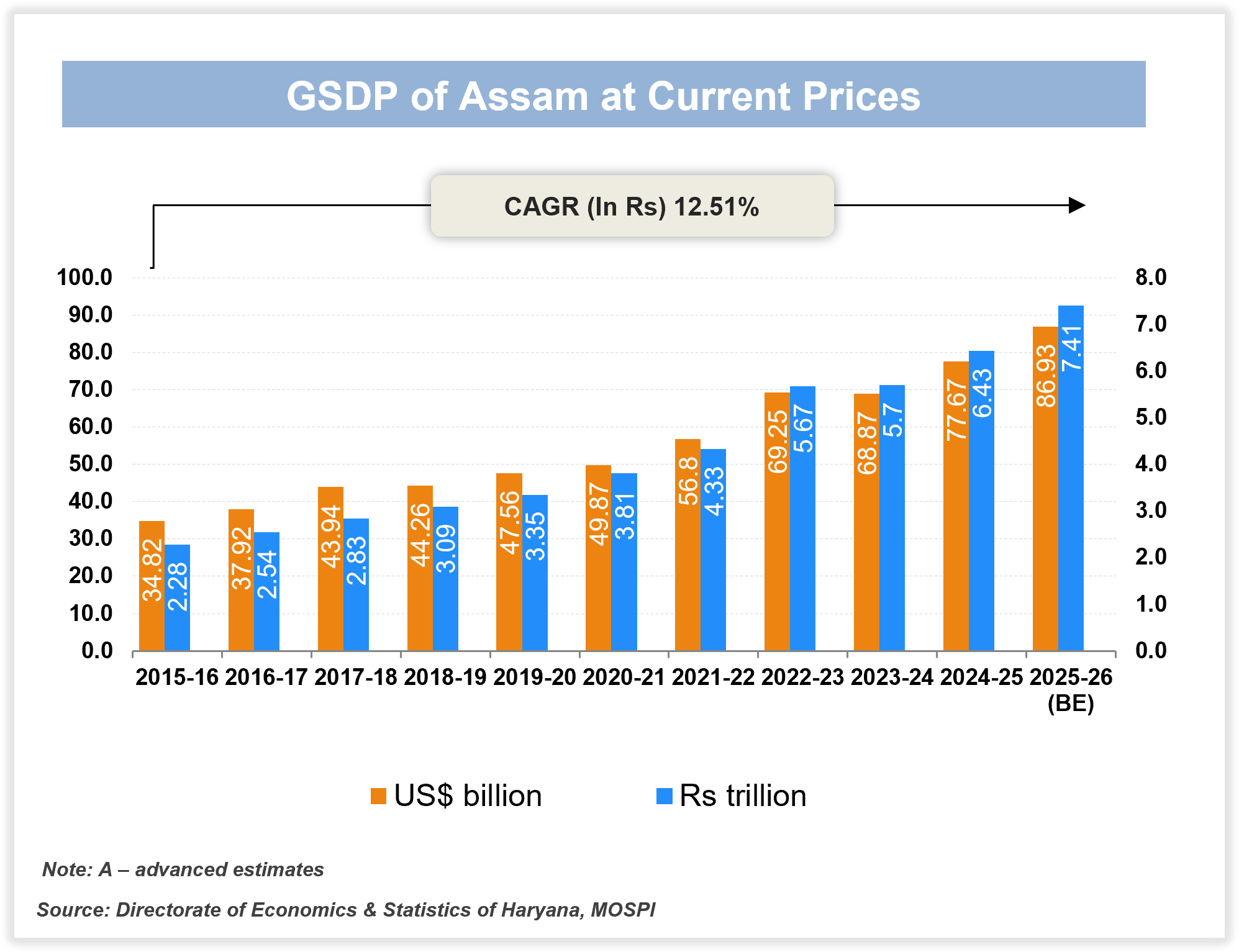
At current prices, the Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Assam is estimated to be at Rs. 7,41,626 crore (US$ 86.93 billion) in FY26.
The GSDP increased at a CAGR of 12.51% between FY16 to FY26.
According to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), FDI inflows for Assam stood at Rs. 212 crore (US$ 23.85 million) from October 2019-June 2025.
Exports from the state stood at Rs.4,883 crore (US$ 550.58 million) in FY25. In FY25, the total tea exports from Assam accounted for Rs. 2,361 crore (US$ 266.23 million), which was 48% of the total exports.
According to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Assam had 26.61 million wireless subscribers and 0.40 million wireline subscribers, as of June 2025.
To facilitate infrastructure support, the State Industries and Commerce Department has sponsored three projects as industrial growth centres at Chariduar, Matia and Chaygaon-Patgaon.
The Assam Government has approved 11 integrated infrastructure development centres across the state. Some of the major initiatives taken by the Government to promote Assam as an investment destination are:
- The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a Rs. 1,109 crore (US$ 125 million) loan agreement on September 22, 2025, to improve urban services and build climate resilience across six districts in Assam. The funds will support infrastructure such as six water treatment plants with a combined capacity of 72 million litres per day, 800 km of water-distribution pipelines, and advanced storm-water management systems in Guwahati’s Bahini Basin. The project also includes institutional reforms such as real-time monitoring to maintain non-revenue water below 20% and build capacity in urban governance.
- The Assam government approved the Assam Agricultural Produce and Livestock Marketing Act on September 9, 2025, aimed at streamlining agricultural and livestock trade across the state, enhancing market access for farmers and rearers.
- The Assam government unveiled a Rs. 25,000 crore (US$ 2.82 billion) plan on May 27, 2025, to boost electronics manufacturing in the state, with a large portion of the funds earmarked for incentivising component makers and attracting investment in key segments such as printed circuit board assemblies and display modules.
- As of February, the Government of India has approved a Rs. 4,800 crore (US$ 541 million) investment package for the transformation of inland waterways in Assam, including Rs. 1,500 crore (US$ 169 million) for the “Harit Nauka” green-vessel initiative by 2030, Rs. 315 crore (US$ 35.5 million) to establish water-metro services in Guwahati and Dhubri, Rs. 120 crore (US$ 13.5 million) for a Regional Centre of Excellence in Dibrugarh and Rs. 100 crore (US$ 11.3 million) for riverine lighthouses along the Brahmaputra river.
- Under State Budget FY26:
- Rs. 9,703 crore (US$ 1.13 billion) has been allocated for capital outlay on roads and bridges.
- Rs. 8,553 crore (US$ 995.9 million) has been allocated for government primary schools and Rs. 6,665 crore (US$ 776.1 million) has been allocated as assistance to non-government secondary schools.
- Rs. 1,316 crore (US$ 153.2 million) has been allocated for urban health services - allopathy.
- Rs. 3,836 crore (US$ 446.7 million) has been allocated for rural health services - allopathy.
- Rs. 1,388 crore (US$ 161.6 million) and Rs. 1,464 crore (US$ 170.5 million) has been allocated for forestry and wildlife.
- The Ministry of Rural Development has approved 78 roads totaling 563.67 km and 14 bridges in Assam under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) - III, with an investment of Rs. 378.68 crore (US$ 45.41 million) to enhance rural connectivity and boost economic growth in the North-Eastern region.
- Union Minister of Ports, Shipping & Waterways, Mr. Sarbananda Sonowal, announced an investment of more than Rs. 645 crore (US$ 77.64 million) for the development of 10 waterways projects in Assam, as part of the flagship Sagarmala program.
- Assam Chief Minister Mr. Himanta Biswa Sarma laid the foundation stone of seven infrastructure projects, including a new Raj Bhavan and Guwahati Police Commissioner's office, worth Rs. 1,776 crore (US$ 216.9 million) in the state capital.
- Under the State Budget 2024-25, Rs. 23,227 crore (US$ 2.81 billion) was allocated for education, sports, art and culture.
- Under the State Budget 2024-25, Rs 6,650 crore (US$ 803.14 million) has been allocated for government primary schools and Rs 5,884 crore (US$ 710.63 billion) has been allocated for assistance to non-government secondary schools.
- According to Chief Minister of Assam, Mr. Himanta Biswa Sarma, the state has 350 hectares of oil palm cultivation, covering Goalpara, Bongaigaon and Kamrup districts, which could be beneficial under the Union Government’s newly launched National Mission on Edible Oils - Oil Palm (NMEO-OP).
- The Government has set a target to generate 6,500 MW of power in the state by 2030.
- Under the ‘Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan’ (CTDP) for the North-eastern region, the Union Cabinet approved the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) scheme to provide mobile coverage in Arunachal Pradesh and two districts of Assam, namely Karbi Anglong and Dima Hasao.
Assam offers a strong and evolving growth story, anchored by its strategic location as India’s gateway to the Northeast and Southeast Asia, abundant natural resources, and rapidly improving infrastructure. Robust GSDP growth, rising public investment in roads, railways, waterways, and urban infrastructure, and targeted policy support are strengthening the state’s economic base. Traditional strengths in tea, oil and gas, and handlooms are being complemented by expanding opportunities in power, tourism, logistics, and services. With increasing connectivity, sustained capital expenditure, and a focus on sustainable and inclusive development, Assam is well positioned to emerge as a key investment and trade hub in eastern India.




