SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (17)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
How Investments Are Fuelling The Growth of E-Commerce in India

E-commerce in India is experiencing an incredible amount of change; it has progressed with leaps and bounds, evolving from a niche service to the modern-day cornerstone of the retailing industry. Although multiple factors such as the increasing internet penetration and the ubiquity of smartphones have contributed to this increase, the main driver behind it has been the strategic and continuous flow of investments. Venture Capitalist and foreign investments have played a crucial role in the development of the infrastructures that support the India e-commerce environment. These capital inflows have triggered a wave of technology, market growth, and it has given rise to a new generation of digital-first brands that are changing shopping and transaction patterns of millions of Indians.
The history of e-commerce in India: A milestone
The history of e-commerce in India is that of gradual, planned development. It started in the late 1990s with early adopters such as FabMart and Rediff.com, who were working in a hostile environment where internet penetration was low, and no one really trusted conducting transactions online. Online marketplaces, such as Flipkart and Snapdeal, began to develop the basic infrastructure and offered a new shopping experience to the Indian consumer in the early 2000s.
The actual inflection point was when the majority of the population started adopting smartphones and low-cost mobile data plans in 2010. It was the period of m-commerce, when a new generation of consumers, especially in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, started using online platforms right through their mobile phones. This trend was further boosted by the adoption of digital payment solutions and e-wallets, along with government efforts such as Digital India and Startup India. The adoption of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) simplified the tax system, and now e-commerce participants can easily work across state borders. The industry is now marked by a proliferation of fast-commerce, direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands, a shift towards hyper-local and personalised shopping experiences, which artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics often drive.
Understanding the e-commerce business models in India
The investments that are generated in the Indian market are channelled towards different models of e-commerce. Each of these models has its own structure and opportunities.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): It is the most popular and most straightforward type, where the business sells to the final consumer. There are players such as Amazon, Flipkart and hundreds of D2C brands in this space. The key features of this model include a high number of transactions and customer experience orientation.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): This model deals with business-to-business transactions. IndiaMART and other leading companies are B2B marketplaces in the business arena that bring together business manufacturers and wholesalers with retailers. The investments in this segment are essential to transform the supply chain into the digital realm and establish a more effective business relationship.
- Consumer to Consumer (C2C): In this model, consumers sell to their fellow consumers, and in most cases, a third-party platform is used. Websites such as OLX and eBay are typical examples. The platform has a low-cost, high-profitability opportunity of earning a commission per transaction.
- Quick-Commerce (Q-Commerce): This is one of the rapidly expanding sub-sectors, and with huge investment, it is aimed at delivering speedy groceries and daily essentials. Apps such as Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart and Zepto are all competing hard, and they are establishing a strong network of dark stores to address the need to satisfy the desire to receive something immediately.
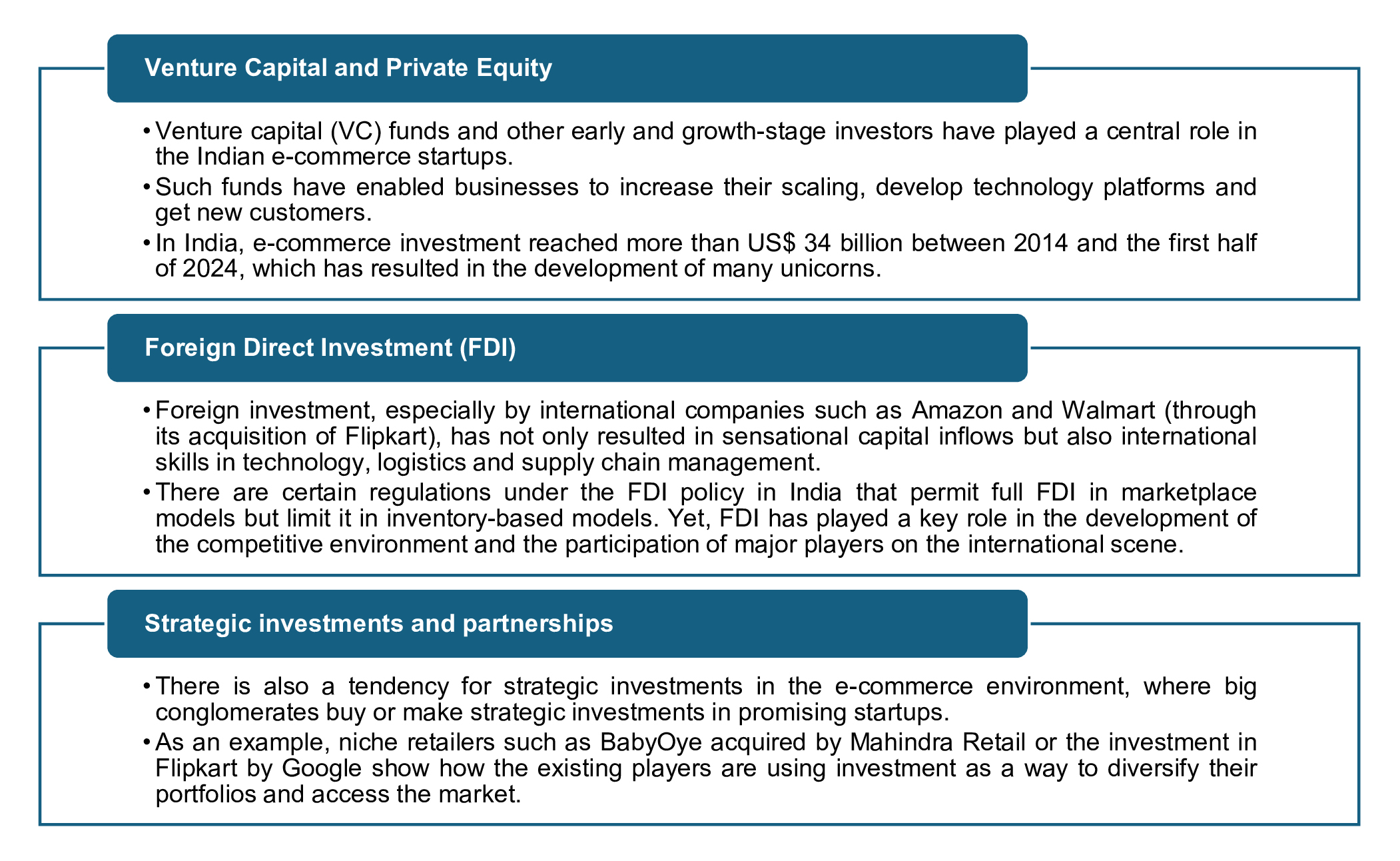
The investment engine: Fueling e-commerce growth
The unprecedented growth of Indian e-commerce directly depends on the inflow of investments. These are not just the capital, but an impetus to innovations, infrastructure and expansion of the markets.
The indispensable need for e-commerce in India
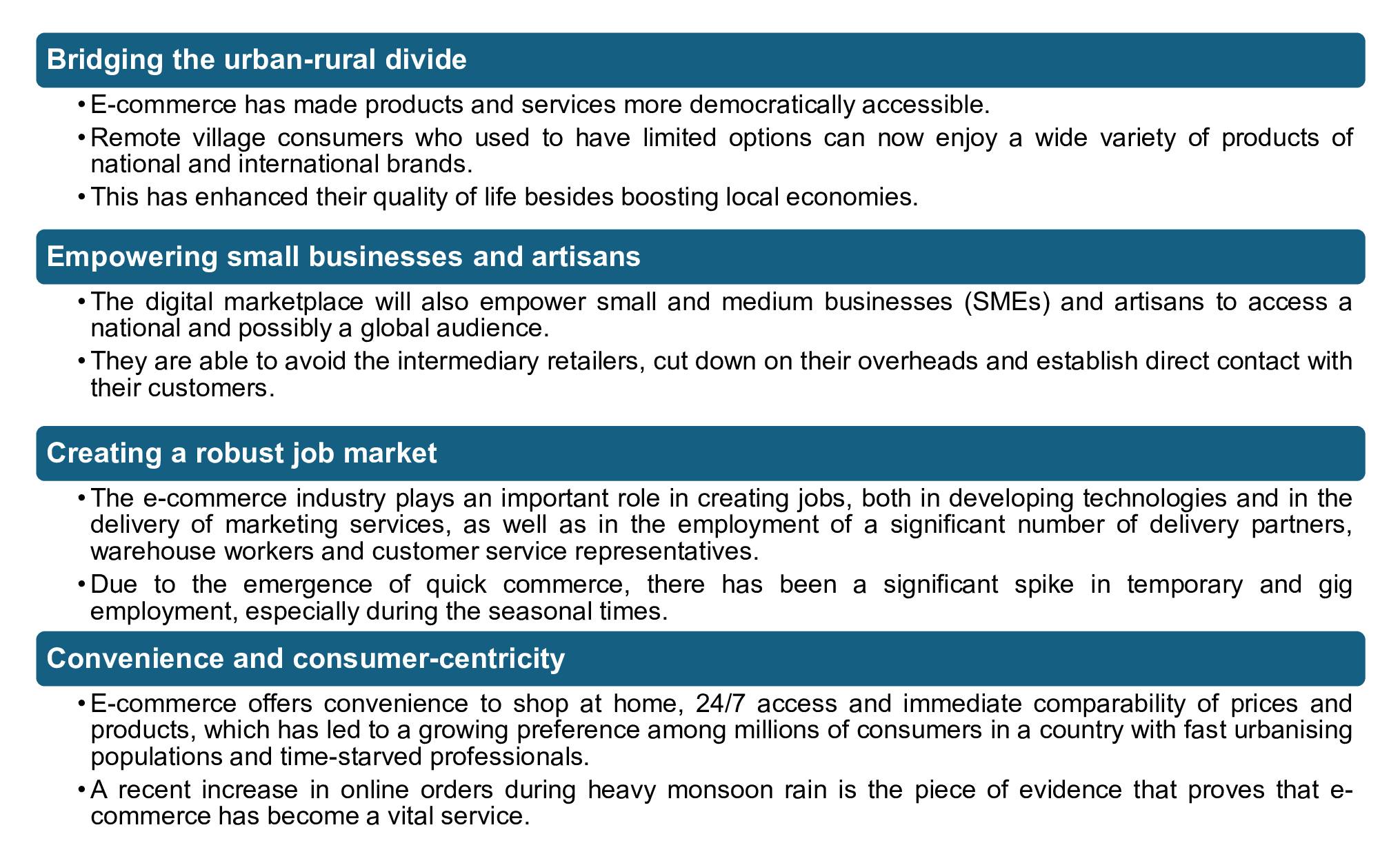
E-commerce is needed in India in a multifaceted way. It is a highly effective instrument of economic and social development as it can solve major business and social issues and generate new possibilities.
The diverse opportunities in India's E-Commerce landscape
The Indian e-commerce market is a canvas of huge opportunities, and it has drawn both domestic and international companies. The market is valued at US$ 136.43 billion in 2025 with a projection of US$ 327.38 billion by 2030 and a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.13% by 2030. This goes to show its potential for exponential growth.
- Growing consumer base: The growing middle class of India, with an increasing disposable income and rising consumer spending on discretionary items, is one of its drivers. Analysts are forecasting a boom in the sales of the festive season, especially with the GST rationalisation of consumer durables in the recent past, which has increased consumer confidence.
- Niche markets and D2C brands: On top of the large players, niche e-commerce can be found. Organic skincare and handicrafts, and targeted B2B marketplaces, are just a few examples of a new generation of D2C brands that are using the internet to forge direct connections with their target market.
- Technological advancement: The implementation of technologies such as AI and machine learning (ML) is opening opportunities for a personalised shopping experience, effective logistics and advanced data analytics. Sustainable business practices, conversational commerce and headless commerce are also becoming critical trends.
- Logistics and supply chain: The e-commerce industry grows, and with it, the need to have an effective and efficient logistics and supply chain network. This industry needs investment in order to deliver on time and provide a smooth customer experience.
The way forward
Summing up, the Indian e-commerce situation could be considered an example of the transformational impact of strategic investments. What started as a fledgling industry with a small customer base has now, with the coming influx of venture capital and FDI, grown in size to become a mainstream economic power. The way ahead for e-commerce in India is characterised by additional innovation and inclusion. This will entail using investments to tap the nation’s huge, untapped rural regions, streamline quick commerce and enable new sets of digitally native D2C brands and social commerce platforms. Besides, by introducing initiatives, such as the Open Network to Digital Commerce (ONDC), the industry will be more democratised, establishing a level playing field for small and medium enterprises. Finally, the active injection of funding, the technological progress and the favourable governmental policies will together be the lifeblood that will drive the Indian e-commerce industry to its target of becoming a worldwide e-commerce force.
FAQs
How has e-commerce transformed shopping in India?
It has democratised access to products and services, bridging the urban-rural divide and offering unprecedented convenience.
What is the primary role of investments in India's e-commerce growth?
Investments act as a catalyst, providing the capital for innovation, technology and logistics that power the entire ecosystem.
What are the key drivers of consumer demand in Indian e-commerce?
A growing middle class, rising disposable incomes and the convenience of shopping from home are the main drivers.
How has the government's "Digital India" initiative impacted e-commerce?
It has accelerated growth by promoting digital literacy, online payments and creating a favourable regulatory environment.
What kind of jobs does the e-commerce sector create in India?
It creates a wide range of jobs, from technology and marketing roles to a large workforce of delivery partners, warehouse staff and gig workers.
















