SEARCH
RECENT POSTS
Categories
- Agriculture (32)
- Automobiles (19)
- Banking and Financial services (34)
- Consumer Markets (51)
- Defence (6)
- Ecommerce (21)
- Economy (69)
- Education (13)
- Engineering (6)
- Exports (21)
- Healthcare (25)
- India Inc. (8)
- Infrastructure (29)
- Manufacturing (28)
- Media and Entertainment (15)
- Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) (15)
- Miscellaneous (30)
- Perspectives from India (34)
- Pharmaceuticals (4)
- Railways (4)
- Real Estate (17)
- Renewable Energy (18)
- Research and Development (9)
- Retail (1)
- Services (6)
- Startups (15)
- Technology (56)
- Textiles (7)
- Tourism (14)
- Trade (5)
Regenerative Medicine in India: The Next Big Leap in Healthcare
- Oct 24, 2025, 14:05
- Healthcare
- IBEF
Imagine a world where damaged tissue can be healed and not just treated. This is the promise of regenerative medicines. This approach is now becoming a part of modern healthcare and India is stepping up to play a major part.
These types of medicine use the body’s natural process to repair, replace or regenerate the affected tissue. It has revolutionised healthcare and changed how we treat diseases and injuries which were previously considered untreatable.
What are regenerative medicines?
The goal of regenerative medicine is to replace or restart the normal functioning of tissues or organs damaged due to age, disease, injury, or other causes. The human body is programmed to automatically heal itself after minor injuries like scrapes and cuts or even major ones like fractures. But certain conditions like heart diseases, cancer, or diabetes that cannot be treated even through medicine, can now can be treated using regenerative medicine. It comprises three distinct approaches:
- Cell-based therapy – This therapy uses cells, particularly stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissue. Stem cells are unspecialised cells that can be divided and developed into various other cells in the body like muscle cells, bone cells or nerve cells. For example, stem cells made into heart muscle cells can be used to treat damaged tissues or cells of the heart.
- Gene editing – Gene therapy is used to alter a defect, replace or introduce new genes inside a cell to treat or prevent a disease. Some known examples of where gene therapy is used include spinal muscle atrophy, sickle cell disease, cancer, immunity disorders, and other genetic conditions.
- Tissue engineering – Tissue engineering involves development of biological substitutes to repair or replace damaged or diseased tissue or organs. For example, tissue-engineered corneas are used to treat patients with corneal blindness or injury.
As different as these approaches look, they often go along with each other. They amplify each other’s capabilities for effective treatment.
Market overview
The global regenerative market was valued at Rs. 2,99,738 crore (US$ 34.56 billion) in 2024 and is projected to reach over Rs. 8,67,300 crore (US$ 100 billion) by 2030.
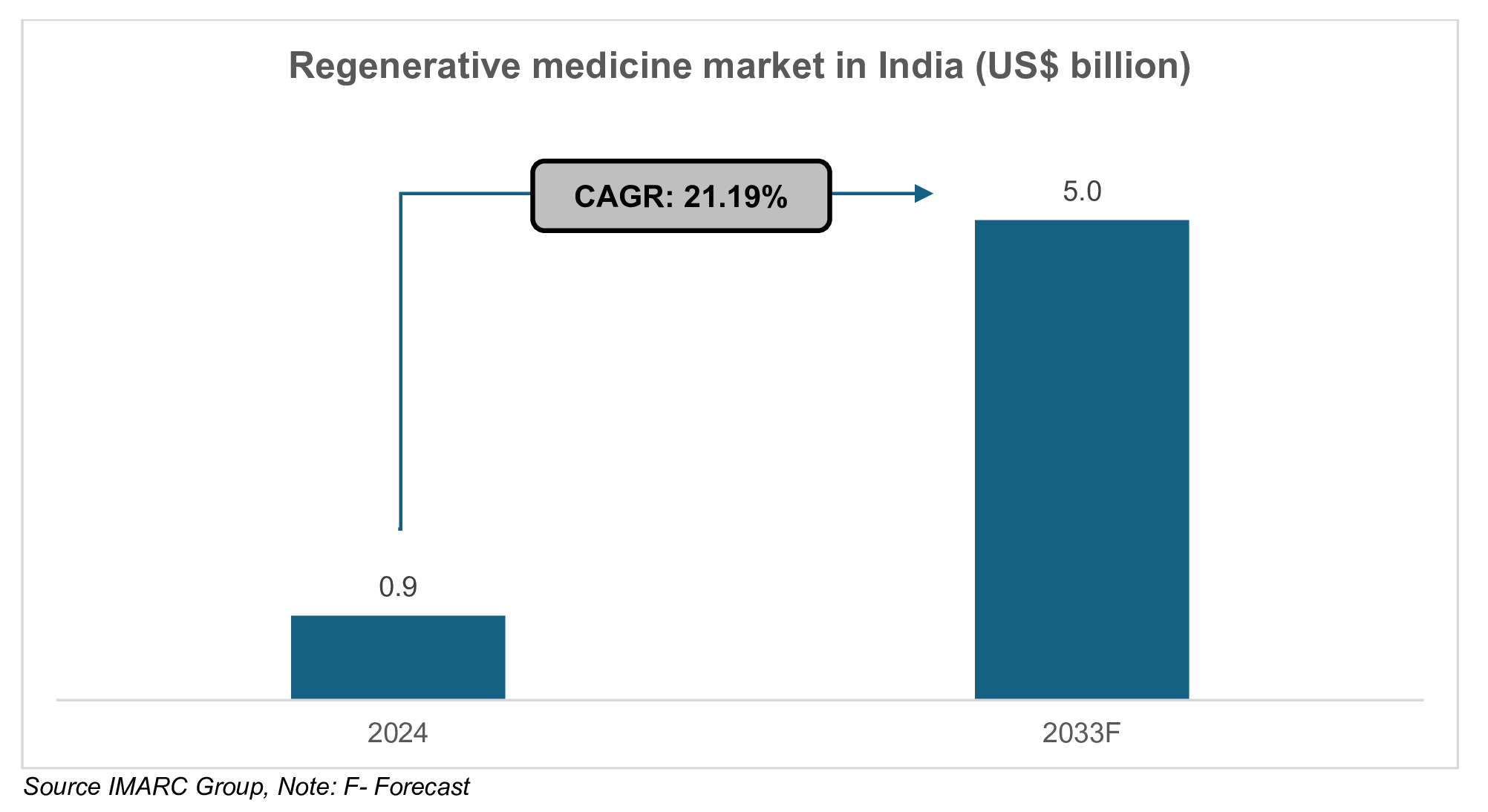
While, as per IMARC Group, in 2024 India’s regenerative medicine market size stood at Rs. 7,641 crore (US$ 881 million) and is expected to reach Rs. 4,33,339 crore (US$ 5 billion) by 2033 exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.19% between 2025 to 2033.
The market is benefiting from rising prevalence of chronic diseases which are key targets for such therapies. With strong government support and increased demand for advanced treatment, India sure could capture a large part of the market.
The country’s low manufacturing cost, rising investment in biotech solutions, and a leading position in generics, makes India an attractive opportunity for both domestic and foreign investors alike.
Recent advancements
India has made significant progress in research and development in the field of regenerative medicine scene:
- Stem cell manufacturing – StemCures a United States based firm, is building India’s largest stem cell manufacturing hub in Hyderabad, Telangana. The hub will entail an investment potential of around Rs. 468 crores (US$ 54 million) and will employ around 150 people. This hub will make high quality treatment more accessible and affordable to the masses.
- CAR-T and cancer cell therapy – The Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay and the Tata Memorial Centre have developed therapies for certain types of blood cancers. They cleared phase one clinical trials and are starting with phase two. CAR-T is a type of modified cells that recognise and attack cancer cells The department of biotechnology has also setup network centres to aid research and development for CAR-T.
- Gene therapy trials – In April 2025, India launched its first ever human gene therapy trial for haemophilia A, a genetic disorder. It was a significant milestone in India’s scientific journey and would mark India joining global efforts in advance cell and gene therapies.
Along with the growth in stem cell therapies, tissue engineering is becoming increasingly prominent in India. Researchers are creating new biomaterials that closely resemble the structure and function of the natural tissues, which offers a promising solution to the shortage of donor organs. Innovations like 3D bioprinting are also gaining ground, which will allow ways to build living tissues form the ground up.
The road ahead
With a large population, a growing number of research centres, and government funded schemes like Biotechnology Ignition Grant Scheme (BIG) of Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), the country could emerge as an exporter of regenerative medicines and biologics to the world. With academic institutions actively engaging in collaborating with regulatory and industrial bodies will create a supportive and inclusive environment for regenerative medicine.
The future of regenerative medicine in India holds immense potential and could revolutionise healthcare. With continued commitment, India can become a market leader in global modern healthcare scene, offering renewed hope and an improved quality of life and could possibly change the lives of millions of people worldwide.
FAQs
What is regenerative medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a treatment approach that helps the body repair or replace damaged tissues using cells, genes or bioengineered materials. It offers new hope for previously untreatable conditions.
What are the main types of regenerative medicine technologies?
There are three key regenerative medicine technologies: stem cell-based therapy, gene editing, and tissue engineering. These often work together to improve healing outcomes.
What is the size of the regenerative medicine market in India?
The regenerative medicine market in India was valued at Rs. 7,641 crore (US$ 881 million) in 2024 and is projected to reach Rs. 4,33,339 crore (US$ 5 billion) by 2033.
How does regenerative medicine offer innovative healthcare solutions?
It provides innovative healthcare solutions by enabling organ regeneration, personalised therapies, and disease reversal, improving recovery and survival rates in complex conditions.
What are the sources of stem cells used in India?
Stem cells in India are sourced ethically from bone marrow, cord blood, and peripheral blood. Use of embryonic stem cells for enhancement is prohibited.
















