Chandigarh
Chandigarh is considered to be one of the best-planned cities in the country. The UT has presence of over 1,150 ancillary units that produce components for tractor industries.
Chandigarh is located at the foothills of the Shivalik hills range in the north and is the capital of Haryana and Punjab. The foundation of the city was laid out in 1952 but assumed its status of capital of Haryana and Punjab during the state reorganization in 1966. Apart from being the capital of Haryana and Punjab, the city is also a Union Territory and hence is governed by the central government.
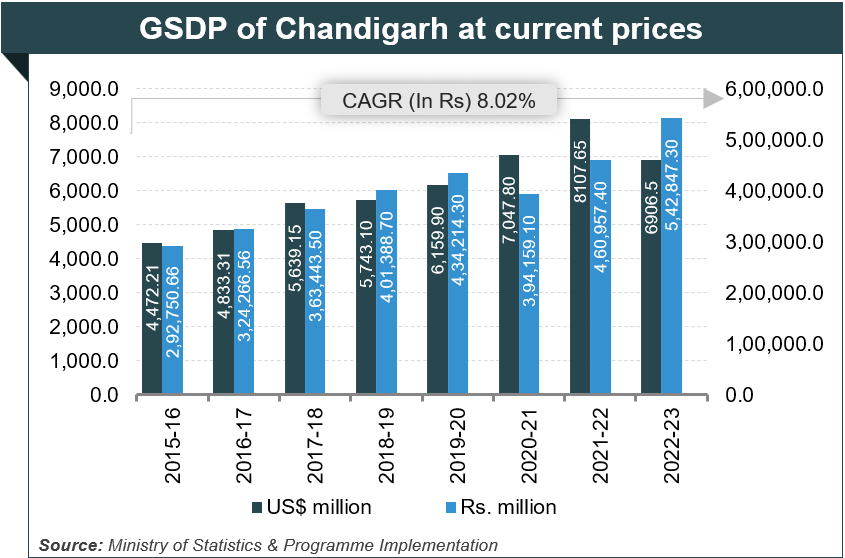
Chandigarh’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) was Rs. 5,42,847.3 million (US$ 6,906.5 million) in 2022-23, rising at a CAGR of 8.02% between 2015-16 and 2022-23.
Some of the recent key developments in Chandigarh are as follows:
Total exports from Chandigarh stood at Rs. 129 crore (US$ 14.5 million) in FY25. The key items exported from Chandigarh include engineering goods, drugs and pharmaceuticals, organic and inorganic chemicals, electronic goods and cotton yarn, fabrics, madeups, handloom products etc.
As of September 2025, Chandigarh had a total installed power generation capacity of 252.82 MW, of which 173.97 MW was contributed by central utilities and 78.85 MW by private utilities.
According to the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Chandigarh had 1.7 million wireless subscribers and 0.12 million wireline subscribers, as of June 2025. Chandigarh had a high Tele-density of 144.09%, as of June 2025.
The Union territory administration has announced a significant increase in property tax rates for both residential and commercial properties within the city. Residential property owners will experience a threefold increase in their tax rates, while commercial property tax rates will be doubled. As a result, the municipal corporation's revenue from property tax is projected to rise from Rs. 45 crore (US$ 5.3 million) to Rs. 90 crore (US$ 10.6 million) annually.
The administration of Chandigarh has been committed to creating a progressive business environment. The city offers a wide range of fiscal and policy incentives for businesses under the Chandigarh Industrial Policy, 2015. The Chandigarh Administration is focusing on promoting the ‘Information Technology’ (IT) industry, which requires less space. To develop the associated ecosystem, the government has developed high-speed data communication facilities for software development and its export by providing a NODE at Punjab Engineering College (PEC), Chandigarh, by collaborating with the Software Technology Parks of India (STPI).
The city has taken several steps to develop its industrial infrastructure and to achieve consistent economic growth. Some of those initiatives are as follows:
- The Chandigarh administration plans to roll out a dedicated micro, small and medium enterprise (MSME) policy by end of 2025 targeting nearly 56,000 units, with incentives, digital infrastructure support and a focus on young and women-led startups under the Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) Scheme.
- On July 15, 2025, a 50-bed critical care hospital was announced for Manimajra, Chandigarh under the Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM), with the Union Government sanctioning Rs. 24 crore (US$ 2.7 million) and the UT Administration allocating 2 acres of land in Pocket 14 for the facility.
- As part of the Union Budget 2024-25, a major chunk of Rs. 875.54 crore (US$ 105 million) has been allocated for the next fiscal year for housing and urban development.
- In the State Budget of 2022-23, Rs. 20,437 lakh (US$ 25.7 million) has been allocated to the buildings & roads department.
- Chandigarh’s total road infrastructure length is 3,269.75 kms and has one national highway with a total length of 15.3 km. The municipal corporation manages 2,440.03 km road network, while PWD manages 537.52 km road network. 163.41 kms road is considered as rural roads.
- Chandigarh is connected through twin track railway lines from Delhi and Mumbai upto Ambala, a single-track broad gauge afterward upto Kalka and a narrow-gauge single track between Kalka and Shimla having heritage value.
- The city has one domestic airport, which is managed by the Ministry of Defence and an international airport. The international airport has the capacity to accommodate 1,600 passengers at a time and is managed (joint venture) by Chandigarh International Airport Limited (CHIAL).
- The Ministry of Natural and Renewable Energy (MNRE) selected Chandigarh to be developed as the ‘Model Solar City’ through Chandigarh Renewal Energy, Science and Technology Promotion Society (CREST) in 2012. The Master Plan for the ‘Model Solar City’ was prepared by The Energy and Resource Institute (TERI) and approved by MNRE in January 2012.
- Chandigarh Industrial Area has been developed over 1200 acres in two phases; Phase I has an area of 776.14 acres and Phase II has an area of 486 acres. Phase III is also being developed with an area of 153 acres.
- Chandigarh's single window system offers a channel for multiple business activities such as pre-establishment approvals, pre-operation approvals, renewal, and investor registration.
Chandigarh is a compact, services-driven Union Territory and the joint capital of Punjab and Haryana, offering a stable and investor-friendly business environment. With a focus on IT, light engineering and pharmaceuticals, its industrial base is dominated by MSMEs, including a strong cluster of ancillary units supporting the tractor and auto component industry. High digital connectivity, reliable power infrastructure and sustained public investment in urban development continue to position Chandigarh as a resilient administrative and economic hub in North India.




