Advantage India
Robust
Demand
* Ministry of New and Renewable Energy targets 500 GW non-fossil-based electricity generation by 2030, as per the Prime Minister's COP26 announcement, with an added installation of 13.5 GW renewable energy capacity in 2023, corresponding to an investment of around Rs. 74,000 crores (US$ 8.90 billion).
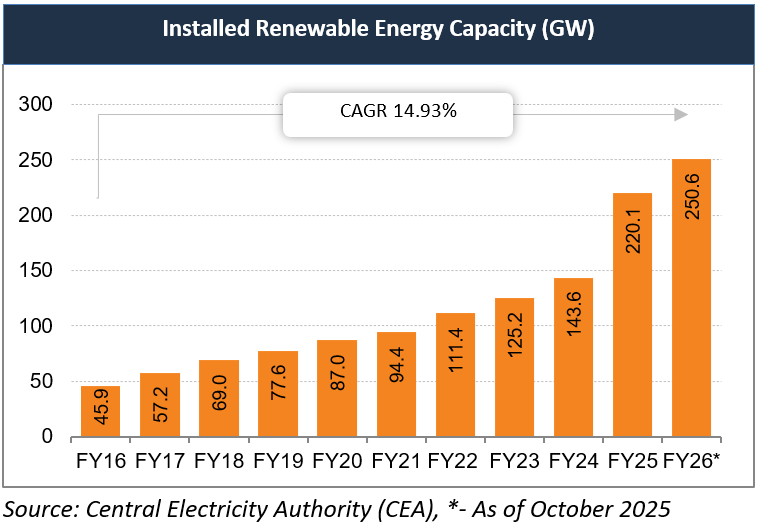
* By October 31, 2025, renewable energy accounted for 39.66% of India’s total installed power capacity, led by solar, which reached 129.92 GW and represented 64.87% of the overall renewable capacity.
Increasing
Investments
* Indian conglomerates plan to invest Rs. 67,42,400 crore (US$ 800 billion) in green hydrogen, clean energy, semiconductors, and EVs by 2034.
* According to Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) from April 2000 to June 2025 non-conventional energy sector attracted Rs. 2,04,341 crore (US$ 23.04 billion) cumulative FDI inflows in India.
Policy
Support
* On October 22, 2025, Coal India Limited signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Indian Institute of Technology Madras to establish a “Centre for Sustainable Energy” focused on developing low-carbon technologies, repurposing coal mines and building human capital for India’s clean-energy transition.
*On August 05, 2025, Hindustan Power has signed a power purchase agreement with Uttar Pradesh Power Corporation Ltd. to set up a 435 MW DC solar power project. The project will supply clean electricity to the state for 25 years, aligning with Uttar Pradesh’s target of achieving 22,000 MW of clean energy capacity by 2026-27.
Competitive
Advantage
*India continues to rank fourth globally in wind power capacity, solar power capacity, and overall renewable energy installed capacity as of FY25, maintaining its position from FY24.
*Power generation from solar and wind projects are likely to be cost-competitive relative to thermal power generation in India in 2025-30.
*India has officially surpassed Japan to become the world's third-largest solar energy producer. According to data from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), India generated 1,08,494 GWh of solar power, exceeding Japan's 96,459 GWh.
Renewable Energy Hubs
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Telangana
- Tamil Nadu

Posters
MORE
TAKING THE CLEAN ROUTE
India is the fourth most attractive country on the renewable energy index globally.
IBEF Campaigns
MORE
Aatmanirbhar Bharat Utsav 2024
Union Minister of External Affairs, Dr. S. Jaishankar and Union Commerce an...
Case Studies
MOREIBEF BLOG
MOREHow Green Hydrogen Will Shape Renewable Energy in India
Green hydrogen, a superior and a more sustainable alternative to fossil fue...
Cooperatives Rising: How Local Communities Are Shaping India’s Growth
The co-operative movement in India is a strong driving force of inclusive d...
India’s Aspirational Districts: Stories of Progress and People-Led Change
India’s Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) was launched in Januar...